Results Of Single Stage Posterior Instrumentation In Complete Traumatic Spondyloptosis Of Thoracolumbar Spine
Abstract
Background: Complete traumatic spinal dislocations above lumbosacral junction are extremely rare injuries. These usually present with complete neural deficit below the level of injury. We present a short series of five patients of such unusual cases of traumatic spondyloptosis who presented to our hospital and were treated with single stage posterior instrumentation.
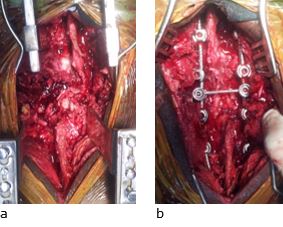
Material & methods: All patients with traumatic spinal injury with complete fracture dislocation i.e. more than 100% subluxation of one vertebra over the other treated with single stage posterior instrumentation were included in the study. Patients were assessed for the neural and bladder recovery, alignment of spinal column, implant loosening, rehabilitation and presence of bedsore.
Result: Five patients with mean age 31 years (range 22 to 36 years) and mean follow-up 14 months (range 12 to 18 months) were included in the study. All patients had with complete neurological deficit at the time of injury and none of patients neural power improved even at final follow-up. None of the patients had any bed sore present. All patients were mobile with the help of brace and wheel chair doning self- intermittent catheterization themselves. Radiologically, in all the patients the spinal column was well aligned, without any loss of alignment or fixation failure.
Conclusion: Traumatic spondyloptosis is an extremely rare severe form on spinal injury presenting with complete neurological deficit. Surgical management by posterior approach is aimed to realign the vertebral column with for proper rehabilitation of patient. Though one cannot expect neurological recovery in these patients but still early restoration of normal spinal cord anatomy should be done to provide proper milieu to the spinal cord and for early rehabilitation to the patient.
Downloads
References
2. Bellew MP, Bartholomew BJ. Dramatic neurological recovery with delayed correction of traumatic lumbar spondyloptosis. Case report & review of literature. J Neurosurg Spine. 2007;6(6):606-10.
3. Cherian I, Dhawan V. Lateral lumbar spondyloptosis. Int J Emerg Med. 2009;2(1):55-6.
4. Abdel-Fattah H, Rizk AH. Complete fracture-dislocation of the lower lumbar spine with spontaneous neurologic decompression. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1990;(251):140-3.
5. Chatani K, Yoshioka M, Hase H, Hirasawa Y. Complete anterior fracture-dislocation of the fourth lumbar vertebra. Spine. 1994;15;19(6):726-9.
6. Chavda DV, Brantigan JW. Technique of reduction and internal fixation of thoracolumbar fracture-dislocation using pedicle screws and variable screw placement plates. Orthop Rev. 1994;l:25-31.
7. Chen WC. Complete fracture-dislocation of lumbar spine without paraplegia. Int Orthop. 1999;23:355–7.
8. Stagner JK. Fracture-dislocation of the thoracolumbar spine with special reference to reduction by open and closed operations. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1947;29(1):107-18.
9. Suomalainen O, Pääkkönen M. Fracture dislocation of the lumbar spine without paraplegia. A case report. Acta Orthop Scand. 1984;55(4):466-8.
10. Wiltse LL, Newman PH, Macnab I. Classification of spondylolisis and spondylolisthesis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1976;117:23-9.
11. Curylo LJ, Edwards C, DeWald RW. Radiographic markers in spondyloptosis: implications for spondylolisthesis progression. Spine. 2002;15;27(18):2021-5.
12. Hanna BG, Pill SG, Drummond DS. Irreducible thoracic spondyloptosis in a child with neurofibromatosis: a rationale for treatment. Spine. 2002;15;27(14):E342-7.
13. Rockower S, McKay D, Nason S. Dislocation of the spine in neurofibromatosis. A report of two cases. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1982;64(8):1240-2.
14. Lehmer SM, Steffee AD, Gaines RW Jr. Treatment of L5-S1 spondyloptosis by staged L5 resection with reduction and fusion of L4 onto S1 (Gaines procedure). Spine. 1994;1;19(17):1916-25.
15. Denis F. The three column spine and its significance in the classification of acute thoracolumbar spinal injuries. Spine. 1983;8(8):817-31.
16. Bosworth DM, Fielding JW, Demarest L, Bonaquist M. Spondylolisthesis; a critical review of a consecutive series of cases treated by arthrodesis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1955;37(4):767-86.
17. Boxall D, Bradford DS, Winter RB, Moe JH. Management of severe spondylolisthesis in children and adolescents. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1979;61(4):479-95.
18. Maurice HD, Morley TR.Cauda equina lesions following fusion in situ and decompressive laminectomy for severe spondylolisthesis. Four case reports. Spine. 1989;14(2):214-6.
19. Peek RD, Wiltse LL, Reynolds JB, Thomas JC, Guyer DW, Widell EH. In situ arthrodesis without decompression for Grade-III or IV isthmic spondylolisthesis in adults who have severe sciatica. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1989;71(1):62-8.
20. Seitsalo S, Osterman K, Poussa M. Scoliosis associated with lumbar spondylolisthesis. A clinical survey of 190 young patients. Spine. 1988;13(8):899-904.
21. Wiltse LL. Spondylolisthesis in children. Clin Orthop. 1961;21:156-63.
22. Maurice HD, Morley TR. Cauda equina lesions following fusion in situ and decompressive laminectomy for severe spondylolisthesis. Four case reports. Spine. 1989;14(2):214-6.
23. Smith MD, Bohlman HH. Spondylolisthesis treated by a single-stage operation combining decompression with in situ posterolateral and anterior fusion. An analysis of eleven patients who had long-term follow-up. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1990;72(3):415-21.
24. Verbiest H.The treatment of lumbar spondyloptosis or impending lumbar spondyloptosis accompanied byneurologic deficit and/or neurogenic intermittent claudication. Spine. 1979;4(1):68-77.
25. Hanley EN Jr, Eskay ML. Thoracic spine fractures. Orthopedics. 1989;12(5):689-96.
26. Sapkas GS, Papagelopoulos PJ, Papadakis SA, Themistocleous GS, Stathakopoulos DP et al. Thoracic spinal injuries: operative treatments and neurologic outcomes. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 2003;32(2):85-8.
27. Shapiro S, Abel T, Rodgers RB.Traumatic thoracic spinal fracture dislocation with minimal or no cord injury. Report of four cases and review of the literature. J Neurosurg. 2002 Apr;96(3 Suppl):333-7.
28. Fountain SS. A single-stage combined surgical approach for vertebral resections. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1979;61(7):1011-7.
29. Gräbe RP. Fracture-dislocation of the lumbosacral spine during a grand mal epileptic seizure. A case report. S Afr Med J. 1988 Aug 6;74(3):129-31.
30. Riska EB, Myllynen P, Böstman O.Anterolateral decompression for neural involvement in thoracolumbar fractures. A review of 78 cases. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1987 Nov;69(5):704-8.
31. Samberg LC.Fracture-dislocation of the lumbosacral spine. A case report. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1975 Oct;57(7):1007-8.
32. Sapkas G, Pantazopoulos T, Efstathiou P.Anteriorly displaced transverse fracture of the sacrum with fracture-dislocation at the L4-L5 lumbar level. Injury. 1985 Mar;16(5):354-7.
33. Van Savage JG, Dahners LE, Renner JB, Baker CC.Fracture-dislocation of the lumbosacral spine: case report and review of the literature. J Trauma. 1992 Nov;33(5):779-84.
34. Prasad VS, Vidyasagar JV, Purohit AK, Dinakar I.Early surgery for thoracolumbar spinal cord injury: initial experience from a developing spinal cord injury centre in India. Paraplegia. 1995 Jun;33(6):350-3.
35. Silvestro C, Francaviglia N, Bragazzi R, Viale GL. Near-anatomical reduction and stabilization of burst fractures of the lower thoracic or lumbar spine. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 1992;116(1):53-9.
36. Han IH, Song GS. Thoracic pedicle screw fixation and fusion in unstable thoracic spine fractures. J Korean Neurosurg. 2002;32:334–40.
37. Park YK, Lee JK, Lim DJ, Chung HS, Lee HK. Pedicle screw fixation of the thoracic spine. J Korean Neurosurg. 1999;28:190–195.
The entire contents of the Orthopaedic Journal of Madhya Pradesh Chapter are protected under Indian and International copyrights. Orthopaedic Journal of Madhya Pradesh Chapter allow authors to retain the copyrights of their papers without restrictions, Authors grant the publisher the right of exclusive publication. The Journal then grants to all users a free, irrevocable, worldwide, perpetual right of access to, and a license to copy, use, distribute, perform and display the work publicly and to make and distribute derivative works in any digital medium for any reasonable non-commercial purpose, subject to proper attribution of authorship. The journal also grants the right to make numbers of printed copies for their personal non-commercial use under Creative Commons Attribution-Non-commercial share alike 4.0 International Public License.

 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative












