Comparative Study between Minimally Invasive Percutaneous Plate Osteosynthesis and Open Reduction Internal Fixation For Management Of Proximal Humerus Fracture
Abstract
Background: Fractures of the proximal humerus comprise nearly 4% of all fractures and 26% of fracture of humerus. Surgical options ranges from open reduction internal fixation (ORIF), intramedullary device fixation, external fixation to hemi arthroplasty. We compared the clinical and radiological outcomes of minimal invasive plate osteosynthesis (MIPO) and open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF) in patients with proximal humerus fractures.
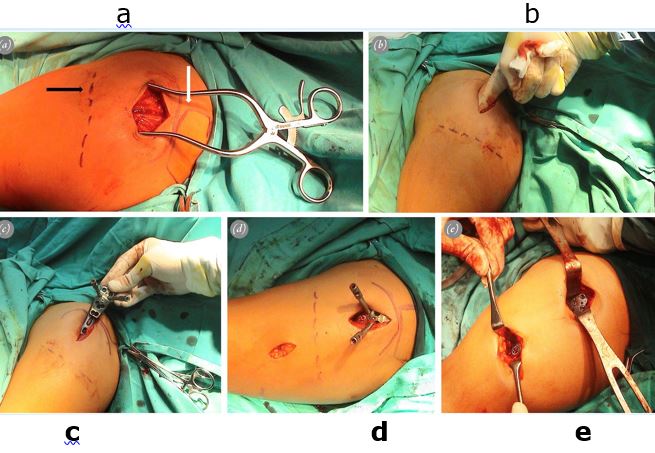
Material & Methods: This prospective study included 24 patients with 2 part and 3 part proximal humerus fracture treated with ORIF or MIPO technique, with 12 patients in each group. A matched pair analysis was performed and patients were followed up for 3 months, 6 months and 12 months both radiographically and clinically using Constant and Murley score.
Results: The average of patients was 47.2 years. Average blood loss and mean duration of surgery was 287.50 ml and 102.9 mins, in ORIF group and 198.33 ml and 93.75 mins in MIPO group. The mean Constant Murley Score at 12 months in the MIPO group was 77.00, while in the ORIF group it was 72.33. MIPO group experienced significantly less pain, higher satisfaction in activities of daily living, and greater range of motion. In the MIPO group, only one patient had infection whereas in ORIF group three patients, had complications with one each having infection, varus collapse and malunion
Conclusion: The use of MIPO with a locking compression plate in the management of proximal humerus fractures is a safe and superior option compared to ORIF.
Downloads
References
2. Court-Brown CM, Caesar B. Epidemiology of adult fractures: A review. Injury 2006;37:691–7.
3. Berkes MB, Little MT, Lorich DG. Open reduction internal fixation of proximal humerus fractures. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med 2013;6(1):47–56.
4. Bjorkenheim JM, Pajarinen J, Savolainen V. Internal fixation of proximal humeral fractures with a locking compression plate: a retrospective evaluation of 72 patients followed for a minimum of 1 year. Acta Orthop Scand 2004;75:741–5.
5. Niemeyer P, Hauschild O, Strohm PC, Muller Ch A, Sudkamp NP, Kostler W. Fracture treatment in the elderly. Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech 2004;71:329–38.
6. Shrader MW, Sanchez-Sotelo J, Sperling JW, Rowland CM, Cofield RH. Understanding proximal humerus fractures: image analysis, classification, and treatment. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 2005;14:497–505.
7. Grawe B, Le T, Lee T, Wyrick J. Open Reduction and Internal Fixation (ORIF) of Complex 3 and 4 Part Fractures of the Proximal Humerus: Does Age Really Matter? Geriatr Orthop Surg Rehabil 2012;3(1):27–32.
8. Solberg BD, Moon CN, Franco DP, Paiement GD. Locked plating of 3- and 4-part proximal humerus fractures in older patients: the effect of initial fracture pattern on outcome. J Orthop Trauma 2009;23:113–19.
9. Edelstein Y, Ohm H, Rosen Y. Metallosis and pseudotumor after failed ORIF of a humeral fracture. Bull NYU Hosp Jt Dis 2011;69(2):188–91.
10. Lau TW, Leung F, Chan CF, Chow SP. Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis in the treatment of proximal humeral fracture. Int Orthop 2007;31:657–64.
11. Liu J, Li SH, Li ZH, Wang JG, Yang CX, Zhang L, et al. Case-control study on minimally invasive percutaneous new plate osteosynthesis applied in proximal humerus fractures in elder patients. Zhongguo Gu Shang 2013;26:4–8.
12. Ku YW. Integration of traditional Chinese and western medicine in the treatment of old limb fracture: report of 94 cases. Chin Med J (Engl) 1978;4:476–80.
13. Wan Hazmy CH, Maizuliana SH, Mastura M, orazlina M. Adequacy of pain relief in closed manipulative reduction of fracture and dislocation. Med J Malaysia 2006.
14. Majed A, Macleod I, Bull AM, Zyto K, Resch H, Hertel R, et al. Proximal humeral fracture classification systems revisited. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 2011;20:1125–32.
15. Olerud P, Ahrengart L, Ponzer S, Saving J, Tidermark J. Internal fixation versus nonoperative treatment of displaced 3-part proximal humeral fractures in elderly patients: a randomized controlled trial. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 2011;20:747–55.
16. Brunner A, Thormann S, Babst R. Minimally invasive percutaneous plating of proximal humeral shaft fractures with the Proximal Humerus Internal Locking System (PHILOS). J Shoulder Elbow Surg 2012;21:1056–63.
17. Hess F, Sommer C. Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis of the distal fibula with the locking compression plate: first experience of 20 cases. J Orthop Trauma 2011;25: 110–15.
18. Jones CB, Sietsema DL, Williams DK. Locked plating of proximal humeral fractures: is function affected by age, time, and fracture patterns? Clin Orthop Relat Res 2011;469:3307–16.
19. Shetty MS, Kumar MA, Sujay K, Kini AR, Kanthi KG. Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis for humerus diaphyseal fractures. Indian J Orthop 2011;45:520–6.
20. Apivatthakakul T, Arpornchayanon O, Bavornratanavech S. Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis (MIPO) of the humeral shaft fracture. Is it possible? A cadaveric study and preliminary report. Injury 2005;36:530–8.
21. Beale B. Orthopedic clinical techniques femur fracture repair. Clin Tech Small Anim Pract 2004;19(3):134–50.
22. Constant CR, Murley AH. A clinical method of functional assessment of the shoulder. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1987;214:160–4.
23. Liu J, Li S, Li Z, Wang J, Yang C, Zhang L, et al. Case control study on minimally invasive percutaneous new plate osteosynthesis applied in proximal humerus fractures in elder patients. Zhongguo Gu Shang 2013;26:4–8.
The entire contents of the Orthopaedic Journal of Madhya Pradesh Chapter are protected under Indian and International copyrights. Orthopaedic Journal of Madhya Pradesh Chapter allow authors to retain the copyrights of their papers without restrictions, Authors grant the publisher the right of exclusive publication. The Journal then grants to all users a free, irrevocable, worldwide, perpetual right of access to, and a license to copy, use, distribute, perform and display the work publicly and to make and distribute derivative works in any digital medium for any reasonable non-commercial purpose, subject to proper attribution of authorship. The journal also grants the right to make numbers of printed copies for their personal non-commercial use under Creative Commons Attribution-Non-commercial share alike 4.0 International Public License.

 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative












