Evaluation Of Cast Index In Predicting The Outcome Of Pediatric Forearm Fractures
Abstract
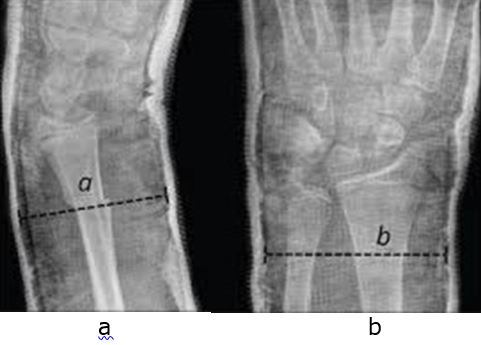
Background: Pediatric forearm fractures of radius ulna account for 40% of all pediatric fracture. Closed reduction followed by application of well molded plaster cast is the standard treatment for these fractures, which can be complicated by re-displacement inside the cast, which further needs re-manipulation or surgery. We assessed the rate if re-displacement in paediatric forearm fractures treated by cast by calculating the cast index.
Material & Methods: 30 patients with fractures of both radius ulna were treated with close reduction and cast application and Cast Index was calculated in immediate post reduction and subsequent radiographs at 2, 4 and 6 weeks. These were evaluated for re-displacement and their relation with cast index.
Results: The mean CI was found to be 0.858. Three patients had re-displacement which required re-manipulation, the mean CI in these re-displacement group was 0.92. Mean CI was found to be higher in proximal third fractures however it did not correspond to increased incidence of re-displacement.
Conclusion: Our study provides sufficient association of cast index in predicting the outcome of pediatric forearm fractures. Higher CI in proximal third fracture didn’t correspond to increased incidence of re-displacement.
Downloads
References
2. Debnath UK, Guha AR, Das S. Distal forearm fractures in children: Cast index as predictor of re-manipulation. Indian J Orthop 2011;45:341-6.
3. Sheikh HQ, Malhotra K, Wright P. Cast index in predicting outcome of proximal pediatric forearm fractures. Indian J Orthop 2015;49:398-402.
4. Garg NK, Ballal MS, Malek IA, Webster RA, Bruce CE. Use of elastic stable intramedullary nailing for treating unstable forearm fractures in children. J Trauma 2008;65:109-15.
5. Zamzam MM, Khoshhal KI. Displaced fracture of the distal radius in children: Factors responsible for redisplacement after closed reduction. J Bone Joint Surg Br 2005;87:841-3.
6. Proctor MT, Moore DJ, Paterson JM. Redisplacement after manipulation of distal radial fractures in children. J Bone Joint Surg Br 1993;75:453-4.
7. Alemdaroðlu KB, Iltar S, Cimen O, Uysal M, Alagöz E, Atlihan D. Risk factors in redisplacement of distal radial fractures in children. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2008;90:1224-30.
8. Chess DG, Hyndman JC, Leahey JL, Brown DC, Sinclair AM. Short arm plaster cast for distal pediatric forearm fractures. J Pediatr Orthop1994;14:211-3.
9. Boyer BA, Overton B, Schrader W, Riley P, Fleissner P. Position of immobilization for pediatric forearm fractures. J Pediatr Orthop 2002;22:185-7.
10. Kamat A, Mutimer J. The cast index: a simple radiological predictor of plaster cast failure in paediatric distal forearm fractures. Orthop Proceedings 2010;92-B(suppl):221-2.
11. Turgut A, Erkuş S, Koca A, Payzıner L, Çiçek AO, Kalenderer Ö. Analysis of the factors causing tight cast syndrome after closed reduction and casting of pediatric distal radius fractures. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2018;52(5):329–333.
The entire contents of the Orthopaedic Journal of Madhya Pradesh Chapter are protected under Indian and International copyrights. Orthopaedic Journal of Madhya Pradesh Chapter allow authors to retain the copyrights of their papers without restrictions, Authors grant the publisher the right of exclusive publication. The Journal then grants to all users a free, irrevocable, worldwide, perpetual right of access to, and a license to copy, use, distribute, perform and display the work publicly and to make and distribute derivative works in any digital medium for any reasonable non-commercial purpose, subject to proper attribution of authorship. The journal also grants the right to make numbers of printed copies for their personal non-commercial use under Creative Commons Attribution-Non-commercial share alike 4.0 International Public License.

 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative












