Effectiveness of Cortical Window Technique for Revision Hip Arthroplasty
Abstract
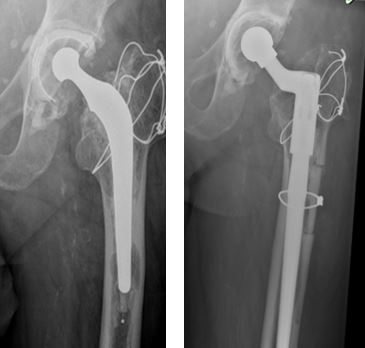
Background: Revision total hip arthroplasty requires removal of cement, cement restrictor and stem followed by canal preparations and reaming. Extraction of femoral component is a challenging problem. There are many techniques being used and described in the literature with all having associated with them. We reviewed the effectiveness of new cortical window method for femoral stem extraction in revision hip arthroplasty.
Material and methods: We retrospective reviewed the result of all our patients operated for revision total hip arthroplasty by cortical window creation in diaphysis of femur for extraction of femoral stem. Window size ranged of 2.5 cm x 5 cm to 2.5 x 7.5cm. We analysed the results for age, indication and type of surgery, size and method of closure of cortical window etc. Outcomes recorded were assessed on pain and mobility.
Results: 13 patients with mean age 76 years (range 60 to 88) with mean time duration of revision surgery with 12.5 years (range 5 to 25 years) were included in study. In 11cases femoral stems (85%) were extracted very easily while in 2 cases it was difficulty. In all cases, except one, the size of cortical window was 2.5 cm x 5 cm. In 10 cases, cable wires were used to fix the cortical window, were as in 3 cases of peri-prosthetic fractures additional plates were used. At 6 months 7 (54%) patients were pain free and 5 (38 %) of patients had mild pain. All patients had good mobility with able to do all daily routine work comfortably.
Conclusion: Cortical window is an acceptable technique which can be used during revision total hip replacement. It can be performed in any age regardless of indication of revision. It reliably allows surgeon to prepare canal by removing all components.
Downloads
References
2. Revell PA. The combined role of wear particles, macrophages and lymphocytes in the loosening of total joint prostheses. J R Soc Interface. 2004;5(28):1263–1278.
3. Field RE, Cronin MD, Singh PJ. The oxford hip scores for primary and revision hip replacement. J Bone Joint Surg. 2004;87B:618-22.
4. Malviya A, Abdul N, Khanduja V. Outcomes following total hip arthroplasty: A review of the registry data. Indian J Orthop. 2017;51:405-13.
5. Hartley WT, McAuley JP, Culpepper WJ, Engh CA Jr, Engh CA Sr. Osteonecrosis of the femoral head treated with cementless total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2000;82(10):1408-13.
6. Maradit Kremers H, Larson DR, Crowson CS, et al. Prevalence of Total Hip and Knee Replacement in the United States. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2015;97(17):1386–1397.
7. Ridgeway S. Infection of the surgical site after arthroplasty of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg. 2005;87B(6):844-850.
8. Schwarzkopf R, Oni JK, Marwin SE. Total hip arthroplasty periprosthetic femoral fractures: a review of classification and current treatment. Bull Hosp Jt Dis. 2013;71(1):68-78.
9. Marsland D, Mears SC. A review of periprosthetic femoral fractures associated with total hip arthroplasty. Geriatr Orthop Surg Rehabil. 2012;3(3):107-20.
10. Paprosky WG, Weeden SH, Bowling JW Jr. Component removal in revision total hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2001;(393):181-93.
11. Wroblewski BM. Current trends in revision of total hip arthroplasty. Int Orthop. 1984;8(2):89-93.
12. Charnley J, Ferreiraade S. Transplantation of the greater trochanter in arthroplasty of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1964;46:191-97.
13. Frankel A, Booth RE Jr, Balderston RA, Cohn J, Rothman RH. Complications of trochanteric osteotomy: long-term implications. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 993;288:209-213.
14. Langlais F, Lambotte JC, Collin P, Langlois F, Fontaine JW, Thomazeau H. Trochanteric slide osteotomy in revision total hip arthroplasty for loosening. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2003;85(4):510-6.
15. Chen WM, McAuley JP, Engh CA Jr, Hopper RH Jr, Engh CA. Extended slide trochanteric osteotomy for revision total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2000;82(9):1215-9.
16. Archibeck MJ, Rosenberg AG, Berger RA, Silverton CD. Trochanteric osteotomy and fixation during total hip arthroplasty. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2003;11(3):163-73.
17. King S, Berend ME, Ritter MA, Keating EM, Faris PM, Meding JB. Extended femoral osteotomy and proximally coated prosthesis for hip revision. Orthop. 2008;31(1):67.
18. Antal I, Szendroi M, Tóth K, Kiss J, Skaliczki G. Retrograde genocephalic removal of fractured or immovable femoral stems in revision hip surgery. Hip Int. 2011;20(1):34-37.
19. Kim YM, Lim ST, Yoo JJ, Kim HJ. Removal of a well-fixed cementless femoral stem using a microsagittal saw. J Arthroplasty. 2003;18(4):511-512.
20. Palumbo BT, Edwards PK, Thatimatla NUK, Bernasek TL. Femoral component incarceration at the distal slot. J Arthroplasty. 2011;26(8):1571e5-1571e7.
21. Melmer T, Steindl M, Schiessel A, Zweymüller K. Fenestration of the femoral shaft: A standard procedure in revision hip surgery without bypassing the cortical defect. Orthopedics. 2004;9(27):965-66.
22. Amanatullah DF, Williams JC, Fyhrie DP, Tamurian RM. Torsional properties of distal femoral cortical defects. Orthopedics. 2014;37(3):158-62.
23. Akrawi H, Magra M, Shetty A, Ng A. A modified technique to extract fractured femoral stem in revision total hip arthroplasty: A report of two cases. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2014;5(7):361-364.
24. Sfeir C, Ho L, Doll BA, Azari K, Hollinger JO. Fracture repair. In: Lieberman JR, Friedlaender GE, editors. Bone regeneration and repair. Humana Press; Totowa, NJ: 2005. pp. 21–44.
The entire contents of the Orthopaedic Journal of Madhya Pradesh Chapter are protected under Indian and International copyrights. Orthopaedic Journal of Madhya Pradesh Chapter allow authors to retain the copyrights of their papers without restrictions, Authors grant the publisher the right of exclusive publication. The Journal then grants to all users a free, irrevocable, worldwide, perpetual right of access to, and a license to copy, use, distribute, perform and display the work publicly and to make and distribute derivative works in any digital medium for any reasonable non-commercial purpose, subject to proper attribution of authorship. The journal also grants the right to make numbers of printed copies for their personal non-commercial use under Creative Commons Attribution-Non-commercial share alike 4.0 International Public License.

 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative












