Outcome of Treatment of unstable intertrochanteric fractures with proximal femoral nail: A retrospective study
Abstract
Background: Intertrochanteric fractures occur frequently in older age groups due to osteoporosis. The main aim of surgery is stable fixation that allows to mobilize the patient early. The treatment of choice for trochanteric fracture remains controversial. Treatment of unstable intertrochanteric fracture is still challenging and are being treated successfully with proximal femoral nail.The purpose of this study is to evaluate the functional and radiological outcome and complications of proximal femoral nail in the treatment of unstable intertrochanteric fractures.
Method: A retrospective study on 100 patients was conducted with unstable intertrochantric fractures treated with Proximal femoral nail .Fracture were classified according to the AO classification system. The fixation used a proximal femoral nail (9-11mm in diameter), a lag screw (85-105 mm in length) and a antirotation pin (10-15 mm shorter than the lag screw). Clinical evaluation was done using Harris hip score and radiologically at 6 weeks, 12 weeks, 6 months, 9 months and thereafter every 6 months.
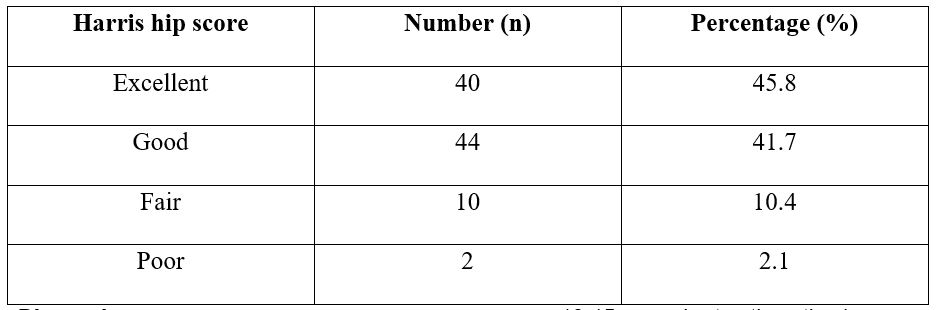
Results: Most of the patients were between 40-60 years (Mean 50.35 years). Most commonly the mode of injury, wrist involvement & fracture type were RTA (50.3%), Right side (60.3%) and AO type C1 . Mean pain score & Function score (PRWE) were less among patients where radiological parameters were restored.
Conclusion: We have suggested that proximal femoral nail offers advantages for the fixation of unstable intertrochanteric fractures with less operative time. It can be easily inserted and provide stable fixation with less complications.
Downloads
References
Anglen JO, Weinstein JN. Nail or plate fixation of intertrochanteric hip fractures: changing pattern of practice. A reviewof the American Board of Orthopaedic Surgery Database. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008; 90(4): 700-707.
Takigami I, Matsumoto K, Ohara A, Yamanaka K, Naganawa T, Ohashi M. et al. Treatment of trochanteric fractures with the PFNA (proximal femoral nail antirotation) nail system. Bull NYU Hosp Jt Dis. 2008; 66(4): 276-279.
Muller ME, Nazarian S, Koch P, Schatzker J. The comprehensive classification of fractures of long bones. 1st ed. Berlin, Heidelberg, Germany, New York, NY, USA: Springer-Verlag 1990.
Orthopaedic Trauma Association Committee for Coding and Classification. Fracture and dislocation compendium. J Orthop Trauma 1996; 10(Suppl 1): v-ix, 1-154.
Cleveland M, Bosworth DM, Thompson FR, Wilson HJ Jr, Ishizuka T. A ten-year analysis of intertrochanteric fractures of the femur. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1959; 41-A: 1399-408.
Baumgaertner MR, Curtin SL, Lindskog DM, Keggi JM. The value of the tipapex distance in predicting failure of fixation of peritrochanteric fractures of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1995; 77: 1058-64.
Lenich A, Mayr E, Rüter A, MöcklCh, Füchtmeier B. First results with the trochanter fixation nail (TFN): a report on 120 cases. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 2006; 126: 706-12.
Moran CG, Wenn RT, Sikand M, Taylor AM. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005;87(3):483–489.
Schipper IB, Steyerberg EW, Castelein RM, van der Heijden FH, den Hoed PT, Kerver AJ, van Vugt AB.J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2004 Jan;86(1):86-94.
Geller JA, Saifi C, Morrison TA, Macaulay W. Tip-apex distance of intramedullary devices as a predictor of cut-out failure in the treatment of peritrochanteric elderly hip fractures. IntOrthop 2010; 34: 719-22.
Nikoloski AN, Osbrough AL, Yates PJ. Should the tip-apex distance (TAD) rule be modified for the proximal femoral nail antirotation (PFNA)? A retrospective study. J Orth Surg Res 2013; 8: 35.
Jin HH, Jong KO, Sang HH, et al. Mismatch between PFNA and medullary canal causing difficulty in nailing of the pertrochanteric fractures. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 2008; 128(12): 1443-6.
Yaozeng X, Dechun G, Huilin Y, Guangming Z, Xianbin W. Comparative study of trochanteric fracture treated with the proximal femoral nail antirotation and the third generation of gamma nail. Injury 2010; 41: 1238.
Boopalan PR, Oh JK, Kim TY, Oh CW, Cho JW, Shon WY. Incidence and radiologic outcome of intraoperative lateral wall fractures in OTA 31A1 and A2 fractures treated with cephalomedullary nailing. J Orthop Trauma 2012;26(11): 638-42.
Gotfried Y. Percutaneous compression plating of intertrochanteric hip fractures. J Orthop Trauma 2000; 14: 490-5.
G.N. Kiran Kumar et al.Treatment of Unstable Intertrochanteric Fractureswith Proximal FemoralNailAntirotation II: Our Experience in Indian Patients,The Open Orthopaedics Journal, 2015, 9, 456-459
Gardenbroek TJ, Segers MJ, Simmermacher RK, Hammacher ER. The proximal femur nail antirotation: an identifiable improvement in the treatment of unstable pertrochanteric fractures? J Trauma 2011; 71: 169-74.
Sahin S, Erturer E, Ozturk I, Toker S, Sec¸kin F, Akman S, Radiographic and functional results of osteosynthesis using the proximal femoral nail antirotation (PFNA) in the treatment of unstable intertrochanteric femoral fractures. Acta OrthopTraumatolTurc 2010; 44: 127-34.
Strauss E, Frank J, Lee J, Kummer FJ, Tejwani N. Helical blade versus sliding hip screw for treatment of unstable intertrochanteric hip fractures. Abiomechanical evaluation. Injury 2006; 37: 984-9.
The entire contents of the Orthopaedic Journal of Madhya Pradesh Chapter are protected under Indian and International copyrights. Orthopaedic Journal of Madhya Pradesh Chapter allow authors to retain the copyrights of their papers without restrictions, Authors grant the publisher the right of exclusive publication. The Journal then grants to all users a free, irrevocable, worldwide, perpetual right of access to, and a license to copy, use, distribute, perform and display the work publicly and to make and distribute derivative works in any digital medium for any reasonable non-commercial purpose, subject to proper attribution of authorship. The journal also grants the right to make numbers of printed copies for their personal non-commercial use under Creative Commons Attribution-Non-commercial share alike 4.0 International Public License.

 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative












