Periprosthetic femoral fracture around the stem of Total Hip Arthroplasty
Abstract
Introduction: Fractures occurring over a hip femoral implant can be divided into intra-operative and post-operative PFFs, and their treatment depends on factors that may severely affect the outcome: level of fracture, implant stability, quality of bone stock, patient’s functional demand, age and comorbidities, and surgeon expertise. Here, we are discussing the results of management of periprosthetic femoral fractures.
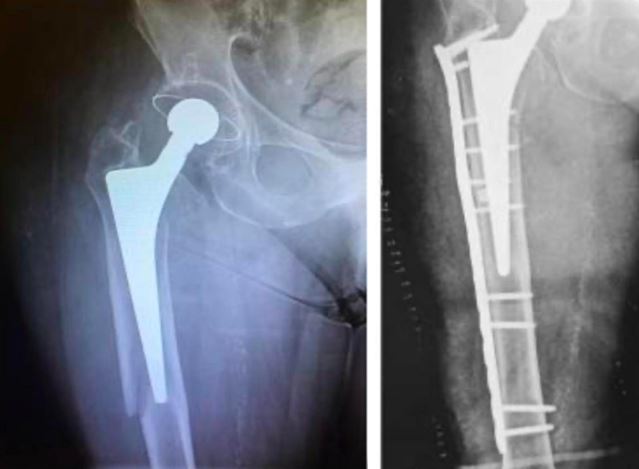
Material and method: Eleven patients of periprosthetic femoral fractures were operated in our hospital in last 3 years. Patients were followed up regularly. Their results were assessed by modified harris hip score. Two fractures were Type A, seven cases were type B and one case was type C fractures. Type A fractures were managed by cables and stainless-steel wires. Type B fractures were managed by long plates, and type C fracture was managed by distal femoral locking plate.
Results: Results were assessed by modified harris hip score. It was found excellent in 3 cases, good in 7 cases and fair in one patient.
Conclusion: In the presence of a well-fixed stem there are various options for retaining the implant and reduction and fixation of the fracture, but loose implants require revision arthroplasty and internal fixation. Future large-scale randomised trials are needed to determine the optimum fixation option with an aim to reduce these complications.
Downloads
References
2. Dominic Davenport1, Jonathan R. Hutt1, Philip A. Mitchell1, Alex Trompeter1, Daniel Kendoff2, Nemandra A. Sandiford1Management of peri-prosthetic fractures around total hip arthroplasty: a contemporary review of surgical options
3. Nikolaos Patsiogiannis,1 Nikolaos K. Kanakaris,1,2 and Peter V. Giannoudis1,2, EFORT Open Rev. 2021 Jan; 6(1): 75–92. Published online 2021 Jan 4. doi: 10.1302/2058-5241.6.200050, Periprosthetic hip fractures: an update into their management and clinical outcomes
4. Periprosthetic fractures, management of the hip and the knee
5. Steven I Rabin, MD, FAAOS; Chief Editor: Murali Poduval, MBBS, MS, Periprosthetic and Peri-implant Fractures Treatment & Management, Updated: Apr 04, 2023
6. Samuel Morgan, Jonathan Bourget-Murray, Simon Garceau, George Grammatopoulos,
Revision total hip arthroplasty for periprosthetic fracture: epidemiology, outcomes, and factors associated with success
7. Parcells B. Hip and Knee Book. 2018;30(2):778. [Google Scholar]
8. Chakravarthy J, Bansal R, Cooper J. Locking plate osteosynthesis for Vancouver Type B1 and Type C periprosthetic fractures of femur: a report on 12 patients. Injury 2007;38:725-33. [Crossref] [PubMed]
9. Dehghan N, McKee MD, Nauth A, et al. Surgical fixation of Vancouver type B1 periprosthetic femur fractures: a systematic review. J Orthop Trauma 2014;28:721-7. [Crossref] [PubMed]
10. Giannoudis PV, Kanakaris NK, Tsiridis E. Principles of internal fixation and selection of implants for periprosthetic femoral fractures. Injury 2007;38:669–687. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
11. Lee YK, Kim JT, Kim KC, Ha YC, Koo KH. Conservative treatment for minimally displaced Type B periprosthetic femoral fractures. J Arthroplasty 2017;32:3529–3532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
12. Capanni F, Hansen K, Fitzpatrick DC, Madey SM, Bottlang M. Elastically suspending the screw holes of a locked osteosynthesis plate can dampen impact loads. J Appl Biomech 2015;31:164–169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
13. Gardner MJ, Nork SE, Huber P, Krieg JC. Less rigid stable fracture fixation in osteoporotic bone using locked plates with near cortical slots. Injury 2010;41:652–656. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
14. Learmonth ID. The management of periprosthetic fractures around the femoral stem. J Bone Joint Surg Br 2004;86:13-9. [Crossref] [PubMed]
15. Tsiridis E, Spence G, Gamie Z, et al. Grafting for periprosthetic femoral fractures: strut, impaction or femoral replacement. Injury 2007;38:688-97. [Crossref] [PubMed]
16. McLean AL, Patton JT, Moran M. Femoral replacement for salvage of periprosthetic fracture around a total hip replacement. Injury 2012;43:1166-9. [Crossref] [PubMed]

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
The entire contents of the Orthopaedic Journal of Madhya Pradesh Chapter are protected under Indian and International copyrights. Orthopaedic Journal of Madhya Pradesh Chapter allow authors to retain the copyrights of their papers without restrictions, Authors grant the publisher the right of exclusive publication. The Journal then grants to all users a free, irrevocable, worldwide, perpetual right of access to, and a license to copy, use, distribute, perform and display the work publicly and to make and distribute derivative works in any digital medium for any reasonable non-commercial purpose, subject to proper attribution of authorship. The journal also grants the right to make numbers of printed copies for their personal non-commercial use under Creative Commons Attribution-Non-commercial share alike 4.0 International Public License.

 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative












