Complications of uncemented total hip replacement in avascular necrosis head of femur, encountered intra and post-operative period
Abstract
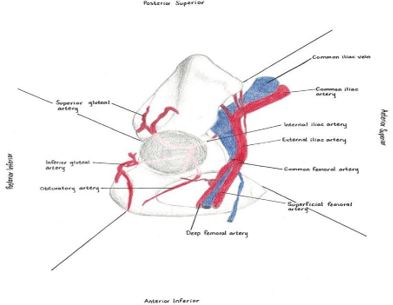
Introduction: Avascular Necrosis Head of Femur is a progressive disorder in which lack of sufficient blood supply leads to cell death, fracture and collapse of the affected area. In stage 3 and 4 patients of AVN of hip, uncemented total hip replacement is the treatment of Choice. The complications in uncemented THR can be intraoperative, postoperative and anaesthetic and also according to time duration can be immediate, early and late.
Material and Method: Fifty-one patients of Avascular necrosis of femoral head of stage III and IV, are operated in last two years by uncemented total hip arthroplasty and their results were assessed by Harris hip score. There are few complications which we encountered in intraoperative and post operative period. The assessment and corresponding solutions of the complications are provided in this study.
Results: The pre-operative modified harris hip score had a mean of 48.51 with a standard deviation of 3.114. The post-operative modified harris hip score increased significantly to a mean of 90.96 with a standard deviation of 3.268. Intraoperative complication like periprosthetic fracture was seen in 3.9% cases only. The majority (92.2%) did not experience any anesthetic complications. Among those who did, 3.9% encountered hypotension and tachycardia, while 2% experienced postoperative nausea and vomiting. Additionally, one patient (2%) suffered from a spinal headache (PDPH). Post-operative complications were present i.e. 5.9% of the patients experienced sciatic nerve injury, and another 5.9% had superficial infections. Additionally, anterior thigh pain, deep infection, and limb length discrepancy each affected 3.9% of the patients, while 2% experienced dislocation.
Conclusion: Uncemented THR is one of the most successful operative procedure done across the globe. The best possible outcome in uncemented total hip replacement surgery can be achieved by appropriate patient selection, appropriate implant size and design, and above all maintaining sterility intra-operatively and during regular dressings and during suture removal.
Downloads
References
2. Lespasio MJ, Sodhi N, Mont MA. Osteonecrosis of the Hip: A Primer. Perm J. 2019;23:18-100. doi: 10.7812/TPP/18-100. PMID: 30939270; PMCID: PMC6380478.
3. Zalavras CG, Lieberman JR. Osteonecrosis of the femoral head: evaluation and treatment. J Am AcadOrthop Surg. 2014;22:455–464. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
4.Melnic CM, Heng M, Lozano-Calderon SA. Acute Surgical Management of Vascular Injuries in Hip and Knee Arthroplasties. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2020 Nov 1;28(21):874-883. doi: 10.5435/JAAOS-D-19-00697. PMID: 32796365.
5. Shields E, Behrend C, Bair J, Cram P, Kates S. Mortality and Financial Burden of Periprosthetic Fractures of the Femur. Geriatric Orthopaedic Surgery & Rehabilitation. 2014;5 (4):147-153. doi: 10.1177/2151458514542281
6.Campbell operative orthopaedics pg no. 265 fourteenth edition
7.Cullen C, Johnson DS, Cook G. Re-admission rates within 28 days of total hip replacement. Ann R Coll Surg Engl 2006;88(5):475 Available at: [Accessed July 16, 2011].
8.Biedermann R, Tonin A, Krismer M, Rachbauer F, Eibl G, Stöckl B: Reducing the risk of dislocation after total hip arthroplasty: the effect of orientation of the acetabular component. J Bone Joint Surg 2005; 87: 762–9
9.Ranawat CS, Rao RR, Rodriguez JA, Bhende HS. Correction of limb-length inequality during total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 2001; 16:71520.
10. Ranawat CS, Rodriguez JA. Functional leg-length inequality following total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 1997;12:359–64.
11. Flecher X, Ollivier M, Argenson JN. Lower limb length and offset in total hip arthroplasty. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2016 Feb;102(1 Suppl):S9-20. doi: 10.1016/j.otsr.2015.11.001. Epub 2016 Jan 18. PMID: 26797005.
12. Campbell‘s Operative Orthopaedics Fourteenth Edition Page No.- 254
13. Saleh KJ, Thongtrangan I, Schwarz EM. Osteolysis: medical and surgical approaches. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2004;(427):138– 47.
14. Rubash HE, Sinha RK, Shanbhag AS, et al. Pathogenesis of bone loss after total hip arthroplasty. Orthop Clin North Am 1998;29(2):173–86.
15. Abu-Amer Y, Darwech I, Clohisy JC. Aseptic loosening of total joint replacements: mechanisms underlying osteolysis and potential therapies. Arthritis Res Ther 2007;9
16. NRJ - Healthcare Quality Improvement Partnership. National Joint Registry 20th Annual Report 2023. Healthcare Quality Improvement Partnership. 2023. Available from: https://www.hqip.org.uk/resource/national-joint-registry-20th- annual-report-2023/
17. New Zealand - Hooper GJ, Rothwell AG, Stringer M, Frampton C Revision following cemented and uncemented primary total hip replacement: a seven-year analysis from the New Zealand Joint Registry. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2009 Apr;91(4):451-8. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.91B4.21363. PMID: 19336803.
18. Swedish Arthroplasty Register Annual Report 2023. Swedish Arthroplasty Register. 2023. Available from: https://registercentrum.blob.core. windows.net/sar/r/SAR_Annual-report-2023_EN- DS5gryeOB.pdf
19. Kakaria HL, Sharma AK, Sebastian B. Total Hip Replacement in Avascular Necrosis of Femoral Head. MJAFI. 2005;61:33-35.
20. Karimi S, Kumar S, Ahmed F, et al. Functional Outcomes of Cementless Total Hip Arthroplasty in Avascular Necrosis of the Hip: A Prospective Study. Cureus. 2020;12(8)
21. Schmalzried, T P; Amstutz, H C; Dorey, F
J. Nerve palsy associated with total hip replacement. Risk factors and prognosis.. The Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery 73(7):p 1074-1080, August 1991.
22. Patsiogiannis N, Kanakaris NK, Giannoudis PV. Periprosthetic hip fractures: an update into their management and clinical outcomes. EFORT Open Rev. 2021 Jan 4;6(1):75-92. doi: 10.1302/2058-5241.6.200050. PMID: 33532088; PMCID: PMC7845569.
23. Peng Z, Lin X, Kuang X, Teng Z, Lu S. The application of topical vancomycin powder for the prevention of surgical site infections in primary total hip and knee arthroplasty: A meta-analysis. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2021 Jun;107(4):102741. doi: 10.1016/j.otsr.2020.09.006. Epub 2020 Nov 27. PMID: 33257290.
24. Rao JP, Bronstein R. Dislocations following arthroplasties of the hip. Incidence, prevention, and treatment. Orthop Rev. 1991 Mar;20(3):261-4. PMID: 2023789.
25. Gordon JE, Davis LE. Leg Length Discrepancy: The Natural History (And What Do We Really Know). J Pediatr Orthop. 2019 Jul;39(Issue 6, Supplement 1 Suppl 1):S10-S13. doi: 10.1097/BPO.0000000000001396. PMID: 31169640.
26. Morshed S, Bozic KJ, Ries MD, Malchau H, Colford JM Jr. Comparison of cemented and uncemented fixation in total hip replacement: a meta-analysis. Acta Orthop. 2007 Jun;78(3):315-26. doi: 10.1080/17453670710013861. PMID: 17611843.
27. Fei C, Wang PF, Wei W, Qu SW, Yang K, Li Z, Zhuang Y, Zhang BF, Zhang K. Relationship between use of screws and acetabular cup stability in total hip arthroplasty: a meta-analysis. J Int Med Res. 2020 Feb;48(2):3000605 209 03649. doi: 10.1177/0300060520903649. PMID: 32054354; PMCID: PMC7111112.
28. Abdulkarim A, Ellanti P, Motterlini N, Fahey T, O'Byrne JM. Cemented versus uncemented fixation in total hip replacement: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Orthop Rev (Pavia). 2013 Mar 15;5(1):e8. doi: 10.4081/or.2013.e8. PMID: 23705066; PMCID: PMC3662257.
29. Tian P, Li ZJ, Xu GJ, Sun XL, Ma XL. Partial versus early full weight bearing after uncemented total hip arthroplasty: a meta-analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2017 Feb 17;12(1):31. doi: 10.1186/s13018-017-0527-x. PMID: 28212661; PMCID: PMC5316222.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
The entire contents of the Orthopaedic Journal of Madhya Pradesh Chapter are protected under Indian and International copyrights. Orthopaedic Journal of Madhya Pradesh Chapter allow authors to retain the copyrights of their papers without restrictions, Authors grant the publisher the right of exclusive publication. The Journal then grants to all users a free, irrevocable, worldwide, perpetual right of access to, and a license to copy, use, distribute, perform and display the work publicly and to make and distribute derivative works in any digital medium for any reasonable non-commercial purpose, subject to proper attribution of authorship. The journal also grants the right to make numbers of printed copies for their personal non-commercial use under Creative Commons Attribution-Non-commercial share alike 4.0 International Public License.

 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative












