Supracutaneous LCP as a definite fixation method in compound metaphyseal and intraarticular fractures of tibia
Abstract
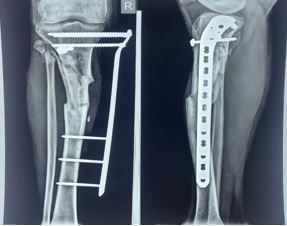
Introduction: Open fractures of distal and proximal tibia are common injuries encountered by orthopedic surgeons. Metaphyseal compound fractures are not suitable for ORIF with greater chances of infection, soft tissue complications and risk of plate exposure. With external fixator, treatment & fracture healing period usually increased & complication rates are quite high, so we managed these fractures by supracutenous LCP as external fixator; and results evaluated. We find out it a better alternative method to conventional external fixator. We evaluated the feasibility of supracutenous LCP as definite fixation methods in open fractures.
Material and methods: This study conducted from April 2020 to October 2023. Total 30 cases were included in this study. Open GA II & IIIA of tibia metaphyseal fractures in 18 cases and intra articular tibia fractures in 12 cases included in this study. Debridement & LCP plates fixation was done in external fixator manner. Proximal & distal tibia LCP fixed with long screws. Most fixations were done within 1 - 5 days of trauma. Patients were followed up till bony union. Minimum follow up was 6 months.
Results: 8 cases united in 4 months, 8 cases united in 6 months, 9 cases united in 6-9 months and 5 cases went in non-union. Average duration of union was 5.6 months. Functional outcomes evaluated by AKSS score for proximal fractures & by AOFAS for distal fractures. 15 cases have shown excellent results; with union, 11 cases have shown good results; soft tissues reconstruction required, 4 cases had bad results; due to infection. Overall, 26 cases were had good to excellent results.
Conclusion: We observed that external fixation in open fractures usually results in infection, delayed or non-union, requirement of further surgeries. Supracutaneous LCP as primary definite fixation can give excellent results in terms of stable & rigid fixation, early fracture union, less chances of second surgery, cost effective and better patient compliance & better functional outcomes.
Downloads
References
2. compression plate as external fixator for intra-articular compound fractures, International Journal of Medical Research & Health Sciences, 2016, 5, 8:62-67
3. Akhil Bansal, Sourabh Alawa, Deependra Sonkar, Arvind Karoria, Anshul Khare and Sanjiv Gaur Supracutaneous locking compression plate as an external fixator in compound metaphyseal and diaphyseal fractures of tibia, International journal of orthopedics science 2020; 6 (3);633-636
4. S. K. Venkatesh Gupta, Shyam Prasad Parimala, Open journal of orthopaedics 2013, 106-109
5. Supracutenous locking compression plate for grade 1 & 2 compound fractures of distal tibia – A case series
6. Rajasekharn , Jai kumar SC, locking compression plate for grade 2 compound fractures of
7. tibia –a case series, International journal of science study 2016,original article;
8. Francesca Giovannini 1, Luigi de Palma 2, Andrea Panfighi 2, Mario Marinelli 2, Intramedullary nailing versus external fixation in Gustilo type III open tibial shaft fractures: a meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials, Strategies Trauma Limb Reconstruction, 2016 Apr;11(1):1-4. doi: 10.1007/s11751-016-0245-7. Epub 2016 Feb 26.
9. Rademakers, Kerkhoffs, Sierevelt, Raaymakers, Marti, Operative Treatment of 109 Tibial Plateau Fractures: Five- to 27-Year Follow-up Results, Journal of Orthopaedic Trauma 21(1):p 5-10, January 2007.
10. Johner R, Wruhs O. Classification of tibial shaft fractures and correlation with results after rigid internal fixation. Clinical orthopaedics and related research. 1983; (178):7 - 25.
The entire contents of the Orthopaedic Journal of Madhya Pradesh Chapter are protected under Indian and International copyrights. Orthopaedic Journal of Madhya Pradesh Chapter allow authors to retain the copyrights of their papers without restrictions, Authors grant the publisher the right of exclusive publication. The Journal then grants to all users a free, irrevocable, worldwide, perpetual right of access to, and a license to copy, use, distribute, perform and display the work publicly and to make and distribute derivative works in any digital medium for any reasonable non-commercial purpose, subject to proper attribution of authorship. The journal also grants the right to make numbers of printed copies for their personal non-commercial use under Creative Commons Attribution-Non-commercial share alike 4.0 International Public License.

 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative












