Primary cemented bipolar hemiarthroplasty in elderly unstable intertrochanteric fractures
Abstract
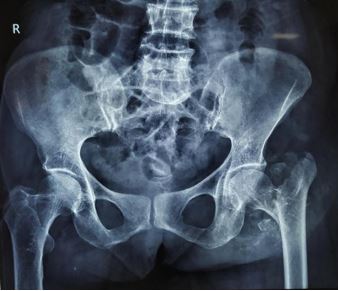
Background: The incidence of inter-trochanteric fractures of the femur is very high in the elderly population. (1) Anatomic restoration of the neck of femur, along with articular congruity is the goal of management.
Materials and Methods: Thirty patients with unstable Intertrochanteric fractures were operated by Bipolar Hemiarthroplasty. Follow-ups were taken at 2, 6, 10 and 16 weeks. Harris Hip Score and FIM score were assessed.
Results: Mean Harris Hip score achieved was 87 at 16 weeks and Mean FIM score achieved was 78.9 at 16 weeks indicating good functional outcomes. The outcome was excellent in 23.4%, Good in 63.3%, Fair in 10% and Poor in 3.3% as per HHS.
Conclusion: This procedure offered pain free mobile hip with early mobilization, easy rehabilitation and early return to functional level, when standard techniques were used.
Downloads
References
Kannus P, Parkkari J, Sievδnen H, Heinonen A, Vuori I, Jδrvinen M. Epidemiology of hip fractures. Bone. 1996;18:57S–63.
Incidence and Economic Burden of intertrochanteric Fracture, JBJS (OA) March28,2019 volume4 – issue 1 p e0045
Arch Osteoporos. Author manuscript PMC 2013 Dec; 8(0): 135. doi:10.1007/s11657-013-0135-2
Marsh JL, Slongo TF, Agel J, Broderick JS, Creevey W, et al.Fracture and dislocation classification compendium: TraumaAssociation classification, database and outcomes committee. JOrthop Trauma. 2007;21:S1-133.
Larsson S. Treatment of osteoporotic fractures. Scand J Surg.2002:91:140-146.
Bannister GC, Gibson AG, Ackroyd CE, Newman JH. The fixationand prognosis of trochanteric fractures: A randomized prospectivecontrolled trial. Clinical Orthop Relat Res. 1990;254:242-6.
Chinoy MA, Parker M). Fixed nail plates, versus sliding hipsystems for the treatment of trochanteric femoral fractures: A metaanalysis of 14 studies. Injury 1999;30:157-63.
Flores LA, Harrington II. Martin H. The stability ofintertrochanteric fractures treated with a sliding screw plate. J BoneJoint Surgery Br. 1990:72:37-40
Sernbo 1, Fredin H. Changing methods of hip fractureosteosynthesis in Sweden: An epidemiological enquiry covering46,900cases. Acta Orthop Scand. 1993;64:173-4.
Larsson S, Friberg S, Hansson LI. Trochanteric fractures: Mobility,complications, and mortality in 607 cases treated with the sliding-screw plate. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1990;260:232–41.
Bess RJ, Jolly SA. Comparison of compression hip screw andgamma nail for treatment of peritrochanteric fractures. J SouthOrthop Assoc. 1997;6:173-9.
Kim WY, Han CH, Park J, Kim JY. Failure of intertrochantericfracture fixation with a dynamic hip screw in relation topreoperative fractures ability and osteoporosis. Intra op.2001;25:360-2.
Jensen JS, Tondevold E, Mossing N. Unstable trochantericfractures treatedthe sliding screw-plate system:biomechanical study of unstable trochanteric fractures. III, ActaOrtho Scand. 1978;49:392-7.
Halder SC. The Gamma nail for peritrochanteric fractures. J BoneJoint Surg: A Br. 1992;74:340–4.
Davis TR, Sher JL, Horsman A, Simpson M, Porter BB, ChekettsRG. Intertrochanteric femoral fractures: Mechanical failure afterinternal fixation. J Bone Joint Surg Br 1990;72:26-31
Thomas AP. Dynamic hip screws that fail Injury. 1991;22:45-46.
Silverton CD, Jacobs JJ, Rosenberg AG, Kull L, Conley A, Galante JO. Complications of a cable grip system. J Arthroplasty. 1996;11:400–404.
The entire contents of the Orthopaedic Journal of Madhya Pradesh Chapter are protected under Indian and International copyrights. Orthopaedic Journal of Madhya Pradesh Chapter allow authors to retain the copyrights of their papers without restrictions, Authors grant the publisher the right of exclusive publication. The Journal then grants to all users a free, irrevocable, worldwide, perpetual right of access to, and a license to copy, use, distribute, perform and display the work publicly and to make and distribute derivative works in any digital medium for any reasonable non-commercial purpose, subject to proper attribution of authorship. The journal also grants the right to make numbers of printed copies for their personal non-commercial use under Creative Commons Attribution-Non-commercial share alike 4.0 International Public License.

 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative












