Evaluation of percutaneous fixation of intra articular fractures of calcaneum using Essex Lopresti manoeuvre
Abstract
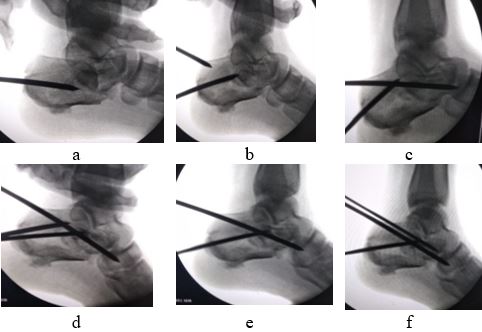
Background: Debate continues regarding the ideal management of calcaneal fractures, between open reduction and internal fixation and closed methods. Open plating has failed to prove its superiority over closed methods owing to poor soft tissue coverage, severe soft tissue swelling, lack of availability of sturdy implants and complications associated with plating. Hence we evaluated the outcome of percutaneous fixation of tongue type intra-articular fracture of calcaneum by Essex Loprestimanoeuvre.
Material and methods: 30 tongue type intra-articular fractures of calcaneum in 23 patients operated by Essex Loprestimanoeuvre by closed reduction and percutaneous pin fixation were assessed functionally by Maryland foot score and radiologically by Bohler’s angle and Gissane’s angle.
Results: 30 calcaneal fractures with mean age 31.6 years and mean follow up of 8.3 months were included in the study. The mean pre-operative Bohler’s angle improved from 8.300 ± 3.84, to 24.470 ± 8.31 immediate postoperatively and to 24.330 ± 8.46 at final follow up of 6 months, respectively. The mean pre-operative Gissane’s angle improved from 134.130 ± 7.03, to 123.150 ± 8.79 immediate postoperatively and to 123.550 ± 8.82 at final follow up of 6 months, respectively. Mean union time was 9 weeks. The mean Maryland Foot Score was 83.43 ± 7.53 (range 61 to 92) and 86 % cases had excellent to good results.
Conclusion: Essex-Lopresti’s method for treatment of tongue-type fractures of calcaneum is easy, cost effective, day care procedure provides stable fixation, early mobilization and excellent results, with low complication rates.
Downloads
References
Buckley RE, Tough S. Displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures. J Am AcadOrthop Surg. 2004 May-Jun;12(3):172-8.
Potter MQ, Nunley JA. Long-term functional outcomes after operative treatment for intra-articular fractures of the calcaneus. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009 Aug;91(8):1854-60.
Khetan VV, Patel I, Modi DR, Panchal N, Bhavsar N, Joshi A. Functional outcome of calcaneal fractures treated by various methods. Niger J Orthop Trauma 2019;18:44-7
Zwipp H, Rammelt S, Barthel S. Calcaneal fractures-open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF). Injury. 2004 Sep;35;Suppl 2:SB46-54.
Pillai A, Basappa P, Ehrendorfer S. Modified Essex-Lopresti / Westheus reduction for displaced intra-articular fractures of the calcaneus. Description of surgical technique and early outcomes. ActaOrthop Belg. 2007 Feb;73(1):83-7.
Tolani A, Desai Y. Management of ComminutedCalcaneum Fractures by Closed Reduction and Percutaneous Fixation-A Case Study. J Orthop Rehab 2015 Jult-Sep;1(2):20-24.
Essex-LoprestiP.Results of Reduction in Fractures of the Calcaneum. J. Bone Joint Surg.1951;33:284.
Essex-LoprestiP.The Mechanism, ReductionTechnique and Results in Fractures of the OsCalcis. Br J Surg.1952;39(157):395–419.
Bohler L. Diagnosis, Pathology and Treatment of fractures of the Oscalcis. J Bone Joint Surg.1931;13:75-89.
Gissane W.Discussion on “Fractures of the OsCalcis”. Proceedings of the British Orthopaedic Association. J. Bone Joint Surg(Am).1947:Jan;(29):254–5.
Tornetta P 3rd. The Essex-Lopresti reduction for calcaneal fractures revisited. J Orthop Trauma. 1998 Sep-Oct;12(7):469-73.
Tornetta P 3rd. Percutaneous treatment of calcaneal fractures. ClinOrthopRelat Res. 2000 Jun;(375):91-6.
Schepers T, Schipper IB, Vogels LM, Ginai AZ, Mulder PG, Heetveld MJ, Patka P. Percutaneous treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures. J Orthop Sci. 2007 Jan;12(1):22-7.
Parikh KN, Moradiya N, Shah S, Khodifad A. Evaluation of results of minimally invasive per cutaneous surgeries in management of calcaneal fractures. Int J Res Orthop 2019;5:81-6.
Arastu M, Sheehan B, Buckley R. Minimally invasive reduction and fixation of displaced calcaneal fractures: surgical technique and radiographic analysis. IntOrthop. 2014 Mar;38(3):539-45.
Tolani A, Desai Y. Management of ComminutedCalcaneum Fractures by Closed Reduction and Percutaneous Fixation-A Case Study. JOrthop Rehab. 2015; 1(2): 20-4.
The entire contents of the Orthopaedic Journal of Madhya Pradesh Chapter are protected under Indian and International copyrights. Orthopaedic Journal of Madhya Pradesh Chapter allow authors to retain the copyrights of their papers without restrictions, Authors grant the publisher the right of exclusive publication. The Journal then grants to all users a free, irrevocable, worldwide, perpetual right of access to, and a license to copy, use, distribute, perform and display the work publicly and to make and distribute derivative works in any digital medium for any reasonable non-commercial purpose, subject to proper attribution of authorship. The journal also grants the right to make numbers of printed copies for their personal non-commercial use under Creative Commons Attribution-Non-commercial share alike 4.0 International Public License.

 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative












