Pre-contoured locking plates vs conventional reconstruction plates in AO type C Distal humerus fractures: A prospective randomised study
Abstract
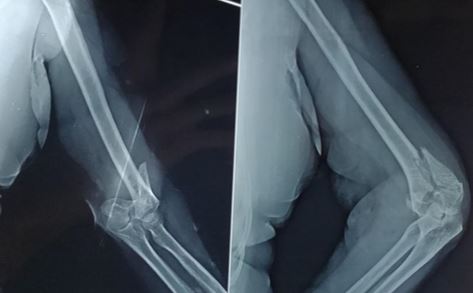
Background: Reconstruction plates have been used from a long time for fixation of distal humerus fractures. Locking plates are increasingly used now-a-days. The aim of this study is to compare the radiological and functional outcome of AO Type C distal humerus fracture treated with pre-contoured locking plates and conventional reconstruction plates.
Material and Methods: A total of 25 patients of AO type C distal humerus fracture were treated using locking plates (n=14) or reconstruction plates (n=11) were compared for radiological union and for functional outcome by Mayo Elbow Performance Score.
Results: The mean duration of surgery and hospital stay was similar in both the groups. The mean Range of motion and MEPS score was significantly higher in locking plate group as compared to conventional reconstruction plates at 3 months post operatively. However both of them were similar at 6 months and 12 months post operatively. 93% union rate in locking plate group and 91 % union rate in reconstruction plate group were seen at the end of 12 months follow-up. Excellent and/or good results were obtained in 93% in locking plate group which is significantly higher than reconstruction plate group in which only 82% patients had excellent and/ or good results.
Conclusion: Locking plates has advantage over reconstruction plates in early mobility and greater functional outcome.
Downloads
References
2. Rose Sh, Melton LJ yo, Morrey BF et al. Epidemiologic features of humeral fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1982;(168):24-30.
3. Helfet DL, Schmeling GJ. Bicondylar intraarticular fracture of the distal humerus In adults. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1993;292:26-36.
4. Wong AS, Baratz ME. Elbow fractures: distal humerus. J Hand Surg [Am]. 2009;34(1): 176-90.
5. Kannus P. Preventing osteoporosis, falls and fractures among elderly people. Promotion of lifelong physical activity is essential. BMJ 1999;318(7178):205-206.
6. Brown RF, Morgan RG. Intercondylar T -shaped fractures of the humerus. Results in ten cases treated by early mobilization. J Bone Joint Surg B1'. 1971;53(3):425-8.
7. Muller WE: Communited fracture of the distal end of the humerus in the adult. AAOS Instructional Coarse Lectures. J Bone Joint Surgery 1964;46A:644.
8. Berkes M, Garrigues G et al. Locking and Non-locking Constructs Achieve Similar Radiographic and Clinical Outcomes for Internal Fixation of Intra-articular Distal Humerus Fractures. HSSJ 2011;7:244-250.
9. Korner J, Diederichs G, ArzdorfM et al. A biomechanical evaluation of methods of distal humerus fracture fixation using locking compression plates versus conventional reconstruction plates. J Orthop Trauma. 2004; 18(5):286-93.
10. Schuster I, Korner J, Arzdorf M, Schwieger K, Diederichs G, Linke B. Mechanical comparison 111 cadaver specimens of three different 90-degree double-plate
osteosyntheses for simulated C2-type distal humerus fractures with varymg bone densities. J Orthop Trauma. 2008;22(2): 113-20.
11. Koshimune M, Kamano M, Takamatsu K, Ohashi H: A randomized companson of locking and non-locking palmar plating for unstable Colles' fractures in the elderly. J Hand Surg [Br]. 2005;30:499-503.
12. Handschin AE, Cardell M, Contaldo C, Trentz 0, Wanner GA: Functional results of angular-stable plate fixation in displaced proximal humeral fractures. Injury.
2008:39:306-313.
13. Jiang R, Luo CF, Wang MC, Yang TY, Zeng BF: A comparative study of Less Invasive Stabilization System CUSS) fixation and two-incision double plating for the treatment of bicondylar tibial plateau fractures. Knee 2008;15:l39-143.
The entire contents of the Orthopaedic Journal of Madhya Pradesh Chapter are protected under Indian and International copyrights. Orthopaedic Journal of Madhya Pradesh Chapter allow authors to retain the copyrights of their papers without restrictions, Authors grant the publisher the right of exclusive publication. The Journal then grants to all users a free, irrevocable, worldwide, perpetual right of access to, and a license to copy, use, distribute, perform and display the work publicly and to make and distribute derivative works in any digital medium for any reasonable non-commercial purpose, subject to proper attribution of authorship. The journal also grants the right to make numbers of printed copies for their personal non-commercial use under Creative Commons Attribution-Non-commercial share alike 4.0 International Public License.

 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative












