Paediatric Tuberculous spinal abscess causing compression at the lumbar level
Abstract
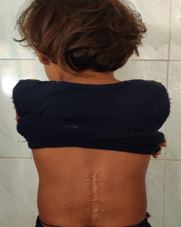
Incidence of paediatric spinal tuberculosis (TB) is increasing. Paediatric spinal TB is known to cause rapid bony destruction and deformity progression. We present a 4-year child with lumbar kyphotic deformity, progressive lower limb weakness and early bladder involvement. Imaging revealed near complete destruction and retropulsion of L4 vertebra with spine at risk signs. Posterior decompression, L1 to S1 fixation with pedicle screws and punching the remaining L4 body ventrally was performed. With aggressive post-operative physiotherapy and AKT patient recovered neurologically from Frankel C to Frankel E grade with complete radiological resolution of disease at final follow-up of 1 year. No further progression of deformity was observed at final follow-up.
Downloads
References
Benzagmout, M., Boujraf, S., Chakour, K., & Chaoui, M. E. F. (2011). Pott's disease in children. Surgical neurology international
Garg RK, Somvanshi DS. Spinal tuberculosis: a review. J Spinal Cord Med. 2011;34(5):440-54. doi: 10.1179/2045772311Y.0000000023. PMID: 22118251; PMCID: PMC3184481.
Teo, H. E., & Peh, W. C. (2004). Skeletal tuberculosis in children. Pediatric radiology, 34(11), 853-860.
Frankel HL, Hancock DO, Hyslop G, Melzak J, Michaelis LS, Ungar GH, Vernon JD, Walsh JJ. The value of postural reduction in the initial management of closed injuries of the spine with paraplegia and tetraplegia. I. Paraplegia. 1969 Nov;7(3):179-92. doi: 10.1038/sc.1969.30. PMID: 5360915.
The entire contents of the Orthopaedic Journal of Madhya Pradesh Chapter are protected under Indian and International copyrights. Orthopaedic Journal of Madhya Pradesh Chapter allow authors to retain the copyrights of their papers without restrictions, Authors grant the publisher the right of exclusive publication. The Journal then grants to all users a free, irrevocable, worldwide, perpetual right of access to, and a license to copy, use, distribute, perform and display the work publicly and to make and distribute derivative works in any digital medium for any reasonable non-commercial purpose, subject to proper attribution of authorship. The journal also grants the right to make numbers of printed copies for their personal non-commercial use under Creative Commons Attribution-Non-commercial share alike 4.0 International Public License.

 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative












