Robotics in Total knee Arthroplasty
Abstract
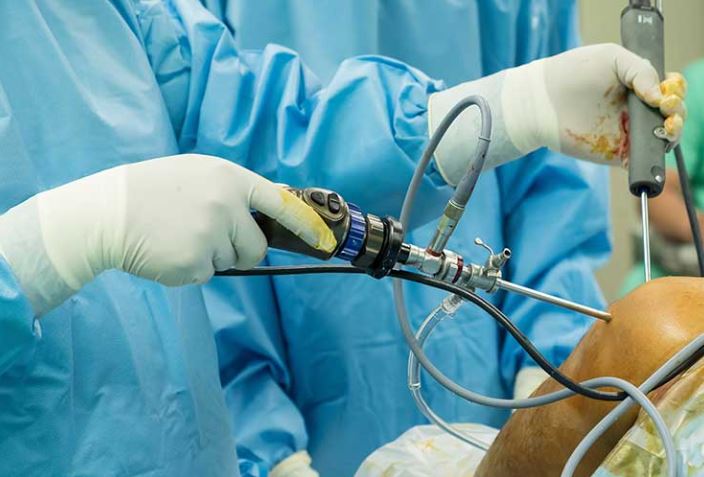
The recent introduction of new robotic systems for total knee arthroplasty (TKA) has created somewhat of a craze. Nevertheless, we can ask ourselves whether it is justified to use these new but very costly technologies. The results and limitations of these robotic tools must be analyzed systematically before confirming their benefits. Most of the newest robotic systems are interactive ones.The term “robotic surgery” refers to the use of programmable devices to perform a wide variety of surgical tasks. These are not intended to replace the surgeon but rather to provide assistance. This activity reviews the role of the interprofessional team in evaluation and treatment using robotic assistance to perform knee arthroplasty. (1)
Downloads
References
2.Hampp EL, Chughtai M, Scholl LY, Sodhi N, Bhowmik-Stoker M, Jacofsky DJ, Mont MA. Robotic-Arm Assisted Total Knee Arthroplasty Demonstrated Greater Accuracy and Precision to Plan Compared with Manual Techniques. J Knee Surg. 2019 Mar;32(3):239-250. [PubMed]
3.Jakopec M, Harris SJ, Rodriguez y Baena F, Gomes P, Cobb J, Davies BL. The first clinical application of a "hands-on" robotic knee surgery system. Comput Aided Surg. 2001;6(6):329-39. [PubMed]
4.Kayani B, Konan S, Tahmassebi J, Pietrzak JRT, Haddad FS. Robotic-arm assisted total knee arthroplasty is associated with improved early functional recovery and reduced time to hospital discharge compared with conventional jig-based total knee arthroplasty: a prospective cohort study. Bone Joint J. 2018 Jul;100-B(7):930-937. [PMC free article] [PubMed]
5.Griffin FM, Insall JN, Scuderi GR. Accuracy of soft tissue balancing in total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2000 Dec;15(8):970-3. [PubMed]
6. Lee GC, Lotke PA. Management of intraoperative medial collateral ligament injury during TKA. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2011 Jan;469(1):64-8. [PMC free article] [PubMed]
7.Khlopas A, Chughtai M, Hampp EL, Scholl LY, Prieto M, Chang TC, Abbasi A, Bhowmik-Stoker M, Otto J, Jacofsky DJ, Mont MA. Robotic-Arm Assisted Total Knee Arthroplasty Demonstrated Soft Tissue Protection. Surg Technol Int. 2017 Jul 25;30:441-446. [PubMed]
8.Kayani B, Konan S, Pietrzak JRT, Haddad FS. Iatrogenic Bone and Soft Tissue Trauma in Robotic-Arm Assisted Total Knee Arthroplasty Compared With Conventional Jig-Based Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Prospective Cohort Study and Validation of a New Classification System. J Arthroplasty. 2018 Aug;33(8):2496-2501. [PubMed]
9. Bautista M, Manrique J, Hozack WJ. Robotics in Total Knee Arthroplasty. J Knee Surg. 2019 Jul;32(7):600-606. [PubMed]
10. Werner FW, Ayers DC, Maletsky LP, Rullkoetter PJ. The effect of valgus/varus malalignment on load distribution in total knee replacements. J Biomech. 2005 Feb;38(2):349-55. [PubMed]
11.Lang JE, Mannava S, Floyd AJ, Goddard MS, Smith BP, Mofidi A, Seyler TM, Jinnah RH. Robotic systems in orthopaedic surgery. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2011 Oct;93(10):1296-9. [PubMed]
12. PanelRégis Pailhé, Total knee arthroplasty: Latest robotics implantation techniques, https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33333275/
13. O. Schneider, J. Troccaz, A six-degree-of-freedom passive arm with dynamic constraints (PADyC) for cardiac surgery application: preliminary experiments, Comput Aided Surg, 6 (2001), pp. 340-351
14. D.J. Jacofsky, M. Allen Robotics in arthroplasty: a comprehensive review, J Arthroplasty, 31 (2016), pp. 2353-2363
15.K.L. Urish, M. Conditt, M. Roche, Orthopedics HR, 2016, Robotic total knee arthroplasty: surgical assistant for a customized normal kinematic knee Orthopedics, 39 (2016), pp. e822-e827,View in ScopusGoogle Scholar
16.W.L. Bargar, A. Bauer, M. Börner, Primary and revision total hip replacement using the Robodoc(R) system, Clin Orthop Relat Res (1976–2007), 354 (1998), p. 82
View in ScopusGoogle Scholar
17.M.H.L. Liow, P.L. Chin, H.-N. Pang, D.K.J. Tay, S.J. Yeo THINK surgical TSolution-One® (Robodoc) total knee arthroplasty Sicot-J, 3 (2017), p. 63,CrossrefView in ScopusGoogle Scholar
18.J.H. Lonner, Y.A. Fillingham, Pros and cons: a balanced view of robotics in knee arthroplasty
J Arthroplasty, 33 (2018), pp. 2007-2013, View PDFView articleView in ScopusGoogle Scholar
19. J.P. van der List, H. Chawla, L. Joskowicz, A.D. Pearle, Current state of computer navigation and robotics in unicompartmental and total knee arthroplasty: a systematic review with meta-analysis, Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc, 24 (2016), pp. 3482-3495
20. B. Kayani, S. Konan, J.R.T. Pietrzak, F.S. Haddad Iatrogenic bone and soft tissue trauma in robotic-arm assisted total knee arthroplasty compared with conventional jig-based total knee arthroplasty: a prospective cohort study and validation of a new classification system J Arthroplasty, 33 (2018), pp. 2496-2501, View PDFView articleView in ScopusGoogle Scholar
21. A. Khlopas, N. Sodhi, A.A. Sultan, M. Chughtai, R.M. Molloy, M.A. Mont Robotic arm-assisted total knee arthroplasty, J Arthroplasty, 33 (2018), pp. 2002-2006 View PDFView articleView in ScopusGoogle Scholar
22. A.A. Sultan, N. Piuzzi, A. Khlopas, M. Chughtai, N. Sodhi, M.A. Mont, Utilization of robotic-arm assisted total knee arthroplasty for soft tissue protection, Expert Rev Med Devices, 14 (2017), pp. 925-927

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
The entire contents of the Orthopaedic Journal of Madhya Pradesh Chapter are protected under Indian and International copyrights. Orthopaedic Journal of Madhya Pradesh Chapter allow authors to retain the copyrights of their papers without restrictions, Authors grant the publisher the right of exclusive publication. The Journal then grants to all users a free, irrevocable, worldwide, perpetual right of access to, and a license to copy, use, distribute, perform and display the work publicly and to make and distribute derivative works in any digital medium for any reasonable non-commercial purpose, subject to proper attribution of authorship. The journal also grants the right to make numbers of printed copies for their personal non-commercial use under Creative Commons Attribution-Non-commercial share alike 4.0 International Public License.

 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative












