Role of Ponseti Technique of Manipulation In Children with Idiopathic Club Foot Presenting After One Year Of Age. A Retrospective Study
Abstract
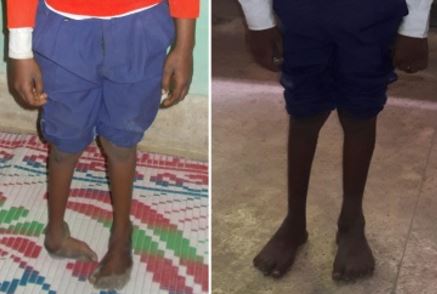
Background: The Ponseti method of manipulation is accepted as a gold standard treatment for idiopathic clubfoot in infants. However, very few studies are available in literature on the use of this method in older children. The aim of this study is to determine the effectiveness of Ponseti manipulation technique in the treatment of late presenters of congenital idiopathic club foot deformity.
Material and Method: We retrospective evaluated the results of 23 children (15 males and 8 females) with 32 clubfeet deformity presenting after the walking age, which were treated with Ponseti manipulation. The outcome assessment was done by Pirani Score. Quantitative variables were expressed as mean ± standard deviation and compared between initial and last follow-up scores using the paired t-test.
Results: The mean age at presentation was 3.4 (range 1 to 15) years. The mean pre-correction total Pirani score was 4.51 (range 2.5 to 6) which improved to mean post-correction total Pirani score of 0.55 (range 0 to 1). This difference was statistically significant (p < 0.001). In 95% of the feet, satisfactory correction of the deformity was achieved. The mean number of casts applied was 9.2 (range 6 to 16). The mean follow-up duration was 14.2 (range 2 to 21) months.
Conclusion: We conclude that the Ponseti technique of manipulation is an effective method for the management of idiopathic clubfoot deformity in older children as well.
Downloads
References
2. Ponseti IV, editor. Treatment. In: Congenital Clubfoot: Fundamentals of Treatment. 1st ed. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 1996. p. 61-97.
3. Morcuende JA. Congenital idiopathic clubfoot: prevention of late deformity and disability by conservative treatment with the Ponseti technique. Pediatr Ann. 2009;35(2):128,132–30.
4. Pirani S, Maddumba E, Mathias R, Kone-Lule J, Penny JN, Beyeza T, Mbonye B, Amone J, Franceschi F. Towards effective Ponseti clubfoot care: the Uganda sustainable clubfoot care project. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009;467:1154–1163.
5. Kelly DM. Congential anomalies of lower extremity. In: Canale ST, Beaty JH, editors. Campbell’s Operative Orthop. 12th ed. St. Louis: Mosby Elsevier; 2008. p. 1078-100.
6. Penny JN. The neglected clubfoot. Tech Orthop. 2005;20:153-66.
7. Lourenço AF, Morcuende JA. Correction of neglected idiopathic club foot by the Ponseti method. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2007;89:378-81.
8. Verma A, Mehtani A, Sural S, Maini L, Gautam VK, Basran SS, et al. Management of idiopathic clubfoot in toddlers by Ponseti's method. J Pediatr Orthop B. 2012;21:79-84.
9. Khan SA, Kumar A. Ponseti's manipulation in neglected clubfoot in children more than 7 years of age: A prospective evaluation of 25 feet with long term follow-up. J Pediatr Orthop B. 2010;19:385-9.
10. Spiegel DA, Shrestha OP, Sitoula P, Rajbhandary T, Bijukachhe B, Banskota AK. Ponseti method for untreated idiopathic clubfeet in Nepalese patients from 1 to 6 years of age. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009;467:1164-70.
11. Pirani S, Hodges D, Sekeramayi F. A reliable method of assessing the amount of deformity. SICOT/SIROT - XXII World Congress 2002 [abstract].
12. Morcuende JA, Dolan LA, Dietz FR, Ponseti IV. Radical reduction in the rate of extensive corrective surgery for clubfoot by using the Ponseti method. Pediatrics 2004;113:376-80.
13. Dobbs MB, Nunley R, Schoenecker PL. Long-term follow-up of patients with clubfeet treated with extensive soft-tissue release. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88:986-96.
14. Ippolito E, Farsetti P, Caterini R, Tudisco C. Long term comparative results in patients with congenital clubfoot treated with two different protocols. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003;85:1286-94.
15. Ponseti IV. Treatment of congenital club foot. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1992;74:448-54.
16. Aronson J, Puskarich CL. Deformity and disability from treated clubfoot. J Pediatr Orthop. 1990;10:109-19.
17. Sinha A, Mehtani A, Sud A, Vijay V, Kumar N, Prakash J. Evaluation of Ponseti method in neglected clubfoot. Indian J Orthop. 2016;50:529-35.
The entire contents of the Orthopaedic Journal of Madhya Pradesh Chapter are protected under Indian and International copyrights. Orthopaedic Journal of Madhya Pradesh Chapter allow authors to retain the copyrights of their papers without restrictions, Authors grant the publisher the right of exclusive publication. The Journal then grants to all users a free, irrevocable, worldwide, perpetual right of access to, and a license to copy, use, distribute, perform and display the work publicly and to make and distribute derivative works in any digital medium for any reasonable non-commercial purpose, subject to proper attribution of authorship. The journal also grants the right to make numbers of printed copies for their personal non-commercial use under Creative Commons Attribution-Non-commercial share alike 4.0 International Public License.

 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative












