A prospective study to compare efficacy of local corticosteroid and platelet rich plasma injection for treatment of lateral epicondylitis
Abstract
Background: Several modalities of management are available for lateral epicondylitis which is a common cause of pain around elbow. Corticosteroid for long time remained gold standard treatment of choice but Studies have suggested the use of platelet rich plasma (PRP) as a safe and effective choice of therapy. Purpose of this study was to evaluate the efficacy of autologous PRP vs steroid injection in treatment of chronic lateral epicondylitis.
Methods: It was a Randomized control trial of 60 cases with at least 6 months of symptoms. PRP was prepared from 40 ml autologous venous blood by double centrifugation method. Patients were followed up to 6 months. All patients had a baseline assessment including Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) and Disability assessment of Shoulder and Hand score (DASH).
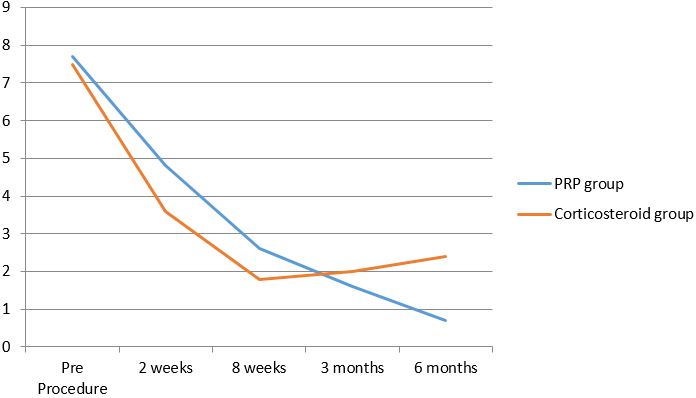
Results: Mean age of patients was 36.5 and 38.3 years for PRP and Corticosteroid group respectively. Success was defined as reduction of pain (VAS) without re-intervention after a follow up of 6 months. Steroid treatment showed better outcome in short term and PRP showed better outcome in long term. Both VAS and DASH score showed significant progressive improvement with no complications with PRP whereas with steroid injection there was recurrence of symptoms after 3 months.
Conclusion: Treatment of patients with Lateral Epicondylitis with PRP decreases pain and significantly increases function, even after a follow-up of 6 months.
Downloads
References
2. Scott A, Khan KM, Roberts CR, Cook JL, Duronio V. What do we mean by the term “inflammation”? A contemporary basic science update for sports medicine. Br J Sports Med 2004 Jun 1; 38(3):372-380.
3. Emilo Lopez Vidriero, Krista A. Goulding, David A. Simon, Mikel Sanchez and Donald H. Johnson. The Use of Platelet-Rich Plasma in Arthroscopy and Sports Medicine: Optimizing the Healing Environment. The Journal of Arthroscopic and Related Surgery 2010; Vol 26, No 2 (February): 269-278.
4. Anitua E, Andia I, Sanchez M, Azofra J, del Mar Zalduendo M, de la Fuente M, Nurden P, Nurden AT. Autologous preparations rich in growth factors promote proliferation and induce VEGF and HGF production by human tendon cells in culture. J Orthop Res 2005 Mar;23(2):281-286.
5. De Mos M, van Windt AE, Jahr H, van Schie HT, Weinans H, Verhaar JA, Van Osch GJ. Can platelet rich plasma enhance tendon repair: a cell culture study. Am J Sports Med 2008 Jun;36(6):1171-1178.
6. Eppley B, Woodell JE, Higgins J. Platelet quantification and growth factor analysis from platelet-rich plasma: Implications for wound healing. Plast Reconstr Surg 2004;114:1502-1508.
7. Sampson S, Gerhardt M, Mandelbaum B. Platelet rich plasma injection grafts musculoskeletal injuries: A review. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med 2008;1:165-174.
8. Scott, A. And Ashe, M.C.(2006) Common tendinopathies in the upper and lower extremities. Current Sports Medicine Reports 5,233-241.
9. Forde, M.S., Punnett, L. and Wegman, H.. (2005) Prevalence of musculoskeletal disorders in union ironworkers. Journal of Occupational and Environmental Hygiene 2, 203-212.
10. Nirschl RP et al Elbow tendinopathy: Tennis elbow, clin sports Med. 2003 oct(4) : 813-36.
11. Karen Walker-Bone, Keith T Palmer and Cyrus Cooper: Occupation and Epicondylitis: A population-based study, Rheumatology (Oxford).2012 Feb. ;51(2) :305-310.
12. Nirschl RP, Ashman ES. Tennis elbow tendinosis (epicondylitis). Instr Course Lect. 2004;53:587–98.
13. Marx RE, Carlson ER, Eichstaedt RM, Schimmele SR, Strauss JE, Georgeff KR. Platelet-rich plasma: growth factor enhancement for bone grafts. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 1998 Jun;85(6):638-646.
14. Molloy T, Wang Y, Murrell GA. The roles of growth factors in tendon and ligament healing. Sports Med 2003 Apr 1; 33(5):381-394.
15. Murray MM, Forsythe B, Chen F, Lee SJ, Yoo JJ, Atala A, Steinert A. The effect of thrombin on ACL fibroblast interactions with collagen hydrogels. J Orthop Res 2006 Mar;24(3):508-515.
16. Marx RE. Platelet-rich plasma: evidence to support its use. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2004;62:489–96.
17. Peerbooms JC, Sluimer J, Bruijn DJ, Gosens T. Positive effect of an autologous platelet concentrate in lateral epicondylitis in a double-blind randomized controlled trial platelet-rich plasma versus corticosteroid injection with a 1-year follow-up. Am J Sports Med 2010 Feb;38(2):255-262.
18. Wong SM, Hui AC, Tong PY, Poon DW, Yu E, Wong LK. Treatment of lateral epicondylitis with botulinum toxin: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Ann Intern Med 2005 Dec 6;143(11):793-797.
19. Boushel R, Langberg H, Green S, Skovgaard D, Bülow J, Kjar M. Blood flow and oxygenation in peritendinous tissue and calf muscle during dynamic exercise in humans. J Physiol 2000 Apr 1;524(Pt 1):305-313.
20. Mishra A, Pavelko T. Treatment of chronic elbow tendinosis with buffered platelet-rich plasma. Am J Sports Med. 2006;34(11):1774-78.
21. Gosens T, Peerbooms JC, van Laar W, den Oudsten BL. Ongoing positive effects of plate-rich plasma versus corticosteroid injection in lateral epicondylitis: A double-blind randomized controlled trial with 2-year follow up. Am J Sports Med. 2011;39(6):1200-08.
22. Omar AS, Ibrahim ME, Ahmed AS, Said M. Local injection of autologous platelet rich plasma and corticosteroid in treatment of lateral epicondylitis and plantar fasciitis: Randomized clinical trial. The Egyptian Rheumatologist. 2012;34:43–49.
The entire contents of the Orthopaedic Journal of Madhya Pradesh Chapter are protected under Indian and International copyrights. Orthopaedic Journal of Madhya Pradesh Chapter allow authors to retain the copyrights of their papers without restrictions, Authors grant the publisher the right of exclusive publication. The Journal then grants to all users a free, irrevocable, worldwide, perpetual right of access to, and a license to copy, use, distribute, perform and display the work publicly and to make and distribute derivative works in any digital medium for any reasonable non-commercial purpose, subject to proper attribution of authorship. The journal also grants the right to make numbers of printed copies for their personal non-commercial use under Creative Commons Attribution-Non-commercial share alike 4.0 International Public License.

 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative












