Functional & radiological outcome of fracture intertrochanter femur treated by Trochanter Femoral Nail
Abstract
Background: Intertrochanteric fractures with varying fracture geometry pose a significant challenge to the treating orthopaedic surgeon. The aim of the study is to evaluate the radiological union and functional outcome in patients of intertrochanteric fracture femur treated with Trochanteric Femoral Nail (TFN)
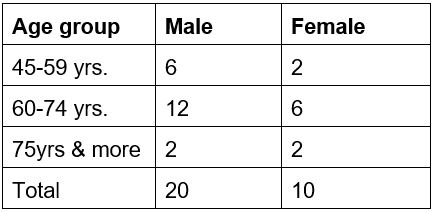
Method: Study of 33 patients with fracture intertrochanteric femur treated by internal fixation using TFN from June 2011 to September 2013. The results were evaluated by assessing the patients regarding radiological union and functional outcome at follow-up as per Modified Harris Hip Score.
Results: Two cases (6.67%) expired during follow up and 1 case (3.33%) did not revert back for follow up. Results were assessed in thirty patients and Harris hip score was excellent in 43.33% patients, good in 36.67% patients and fair in 10 %patients.
Conclusion: Trochanter Femoral Nail is a suitable implant for management of intertrochanteric fractures of femur.
Downloads
References
Kempf I, Grosse A, Taglang G, Favreul E. Gamma nail in the treatment of closed trochanteric fractures, results and indications apropos of 121 cases. Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot. 1993;79:29–40.
Leung KS, So WS, Shen WY, Hui PW. Gamma nail and Dynamic Hip Screw for Peritrochanteric fractures: A randomized prospective study in elderly patients. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1992;74:345–51. [PubMed]
Leung KS, Chen CM, So WS, Sato K, Lai CH, Machaisavariya B, et al. Multicenter trial of modified gamma nail in East Asia. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1996;323:146–54.
Evans E. The treatment of trochanteric fractures of the femur. JBJS 1949;31B 190-203
Harris WH. Traumatic arthritis of the hip after dislocation and acetabular fractures: Treatment by mould arthroplasty. An end result study using a new method of result evaluation. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1969;51-A(4):737-755
Gallangher JC,Melton LJ,Riggs BL et al. Epidemiology of fractures of the proximal femur in Rocester,Minnesota. Clinical Orthop 1980; 150:163-171
Boyd HB and Griffin LL: Classification and treatment of trochanteric fractures. Arch Surg 1949;58:853-866.
Cleveland : A ten year analysis of intertrochanteric fractures, JBJS 63B, 218,1983.
Cummings SR, Nevitt MC. Non- skeletal determinants of fractures: the potential importance of mechanics of falls. Osteoporosis Int 1994; supll: S67-70.
Koval KJ, Aliaroeoff GB, Rokito AS, Lyon T, Zuckermann JD. Patients with femoral neck and intertrochanteric fractures: Are they the same? Clin Orthop.1996; 330:166-172
B. Mall, Susheel kumar Pathak, Vineet Malhotra : Role of dynamic compression hips screw in trochanteric fracture of femour. Indian Journal of Orthopaedics, Vol. 33 No. 3, 226-228, July 1999.
Kulkarni GS : Treatment of trochanteric fractures of hip by modified Richard's compression and collapsing screw, Indian Journal of Orthopedics, vol. 18, No. 1, 30,1984.
Harrington K.D and Johnson J.O., the management of communited unstable intertrochanteric fractures J.B.J.S 55A:1367:1973.
Juluru P Rao, Manuel T. Banzon, Andrew B Wiess : Treatment of unstable intertrochanteric fracture with anatomic reduction and compression hip screw. Clin Orthop and related research, No. 175, 65 - 78 May 1983
Luis A. Flores et al, The stability of intertrochanteric fractures treated with a sliding screw plate, JBJS (Br) 1990, 72-B, 37-40.
Simon H. Bridle fixation of intertrochanteric fractures of the femur (JBJS-Br) 1991, 73 B, 330-4.
Christopher I Adams J Orthop Trauma. 2001 Aug;15(6):394-400.Prospective randomized controlled trial of an intramedullary nail versus dynamic screw and plate for intertrochanteric fractures of the femur. Adams CI1, Robinson CM, Court-Brown CM, McQueen MM.
Zhiyong et al Z Yi, W Ze, G Zhi-yong, et al. Treatment of Femoral Intertrochanteric Fractures With Hemi-hip Prosthesis Replacement in Elderly Patients. Journal of Occupational Health and Damage. 2011;3:172–75.
The entire contents of the Orthopaedic Journal of Madhya Pradesh Chapter are protected under Indian and International copyrights. Orthopaedic Journal of Madhya Pradesh Chapter allow authors to retain the copyrights of their papers without restrictions, Authors grant the publisher the right of exclusive publication. The Journal then grants to all users a free, irrevocable, worldwide, perpetual right of access to, and a license to copy, use, distribute, perform and display the work publicly and to make and distribute derivative works in any digital medium for any reasonable non-commercial purpose, subject to proper attribution of authorship. The journal also grants the right to make numbers of printed copies for their personal non-commercial use under Creative Commons Attribution-Non-commercial share alike 4.0 International Public License.

 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative












