Management of Soft Tissue Complications Associated with Leg Bone Injuries by Local Muscle Pedicle Flap
Abstract
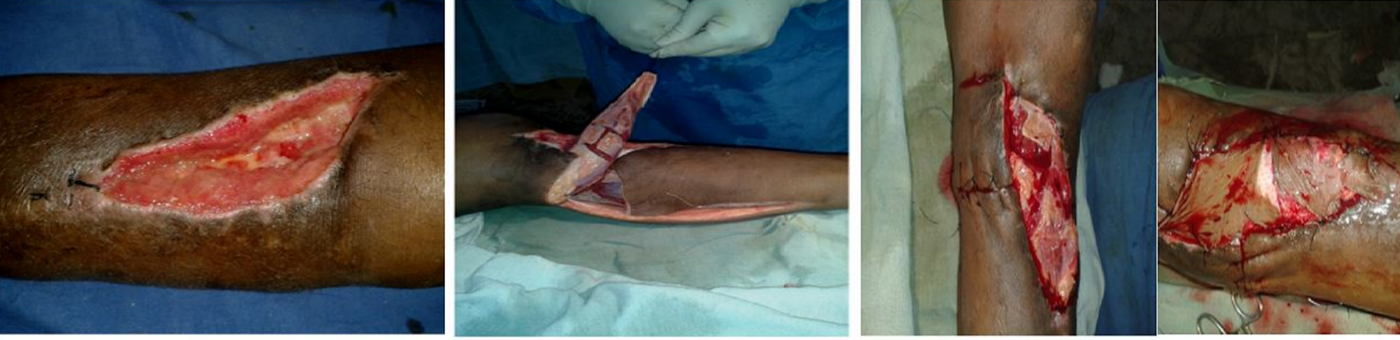
Background: Subcutaneous nature of tibia and poor blood supply to leg bone area causes increased complications and poor wound healing which can be managed by applying principles of plastic surgery
Aims & objectives: To evaluate the use of gastrocnemius, soleus and sural flap by orthoapedic surgeon in management of complications of open leg bone fractures i.e. exposed implants, soft tissue defects.
Material & methods: We prospectively studied 20patients with soft tissue complications in patients having both bone leg fracture. Out of which12 patients were managed by gastrocnemius flap,5 patients by soleus flap & 3 patients were treated by sural flap according to the location of the wound. Patients with age between 18-60 years with no or minimal infection, size of wound <50cm2 for middle leg and <9×12cm for lower leg were included in study. The mean follow up was of 6 months.
Results: Only two sural flap and one soleus flap had marginal necrosis. Hypoaesthesia over lateral border of foot was noted in two patients of sural flap which was not troublesome. Not any patient had developed significant functional loss. All flaps resulted in a good wound coverage with early healing.
Conclusions: Local muscle flap is efficient and easy method of treating wound defects over leg and allows an orthopaedician to manage the compound fractures comprehensively.
Downloads
References
Bucholz RW, Heckman JD, CourtBrown CM. Rockwood and Green's Fractures in Adults 7th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2009 ; pp. 376–7.
Ger R. The technique of muscle transposition in the operative treat¬ment of traumatic and ulcerative lesion of leg. J Trauma 1971; II 6: 502-510
Colen L, Mathes S. Lower extremity traumatic injury. In: Jurkiewicz MJ, Krizek T, Mathes S, Ariyan S, editors. Plastic Surgery. St. Louis: CV Mosby; 1990. p. 935-81
Wright JK, Watkins RP. Use of the soleus muscle flap to cover part of the distal tibia. Plast Reconstr Surg 1981;68:957-8
Rios-Luna, Villanueva-Martinez, Fahandezh-Saddi, Villanueva López, Del Cerro-Gutierrez. Versatility of the sural fasciocutaneous flap in coverage defect of the lower limb. Injury 2007;38:824-31
Heller L, Levin LS. Lower extremity microvascular reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2002;108(4):1029–41.
Alam MK, Shaheen MS, Hossain S, Anam S, Rahman S. Sural Island Flap – A Good Option For Coverage Of The Exposed Heel (Tendoachillis). J Dhaka Med. Coll. 2010;19(1):19-24.
Arnold PG, Yugueros P, Hanssen AD. Muscle flaps in osteomyelitis of the lower extremity: a 20 year account. PlastReconstr Surg. 1999;104(1):10710
Davis KM. et al, Muscle-bone interactions during fracture healing. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact 2015;15(1):1-9
Harry Lorraine E, Miael F, Ewa M. Comparison of the Vascularity of Fasciocutaneous Tissue and Muscle for Coverage of Open Tibial Fractures. Plast Recons Surg: 2009;124:121119
Sanders R, O’neill T. The Gastronmius Myocutaneus Used as A Cover for the Exposed Knee Prosthesis. JBJS: 1981;63-B:383-86. Http://Www.Boneandjoint.Org.Uk/Content/Jbjsbr/63-B/3/383.Full.Pdf
Mathes SJ, Nahai F. Clinical applications for muscle and musculocutaneous flaps. New York; CV Mosby Company Publishers. 1982 : 16-26, 514-524
G.G. Hallock. Getting the most from the soleus muscle. Am Plast Surg, 36 (1996), pp. 139–146
Ata-ul-Haq, Tarar MN, Malik FS, Khalid K, Riaz A, Mehrose MY, Khan H. Hemisoleus muscle flap, a better option for coverage of open fractures involving middle third of tibia. J Ayub Med Coll Abbottabad. 2009 Oct-Dec;21(4):154-8
Ademola SA, Adebayo WO, Lawani O. Reconstruction of soft tissue defects in the distal third of leg,ankle, and foot: A meta-analysis. Nigerian J Plast Surg 2015;11:1-7
Masquelet AC, Romana MC, Wolf G. Skin island flaps supplied by the vascular axis of the sensitive superficial nerves: anatomic study and clinical experience in the leg. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1992;89:1115–21
Pirwani MA, Samo S, Soomro YH. Distally Based Sural Artery Flap: A workhorse to cover the soft tissue defects of lower 1/3 Tibia and Foot. Pak J Med Sci. 2007;23:103-7
Hasegawa M, Torii S, Katoh H, Esaki S. The distally based superficial sural artery flap. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1994 Apr;93(5):1012-20
Kramers-de Quervain IA, Läuffer JM, Käch K, Trentz O, Stüssi E. Functional donor-site morbidity during level and uphill gait after a gastrocnemius or soleus muscle-flap procedure. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2001 Feb;83-A(2):239-46
Neale HW, Stern PJ, Kreitein JG et al. Complications of muscle flap transpositions for traumatic defects of leg. Plastic Reconstr Surg 1983; 72: 512-515.Schemitsch EH, Bhandari M. Fractures of the diaphyseal humerus. Skeletal trauma, 3rd edn. WB Saunders, Toronto. 2001:1481-511.
The entire contents of the Orthopaedic Journal of Madhya Pradesh Chapter are protected under Indian and International copyrights. Orthopaedic Journal of Madhya Pradesh Chapter allow authors to retain the copyrights of their papers without restrictions, Authors grant the publisher the right of exclusive publication. The Journal then grants to all users a free, irrevocable, worldwide, perpetual right of access to, and a license to copy, use, distribute, perform and display the work publicly and to make and distribute derivative works in any digital medium for any reasonable non-commercial purpose, subject to proper attribution of authorship. The journal also grants the right to make numbers of printed copies for their personal non-commercial use under Creative Commons Attribution-Non-commercial share alike 4.0 International Public License.

 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative












