Comparative Analysis of results between Conventional and Accelerated Ponseti Technique for idiopathic congenital clubfoot
Abstract
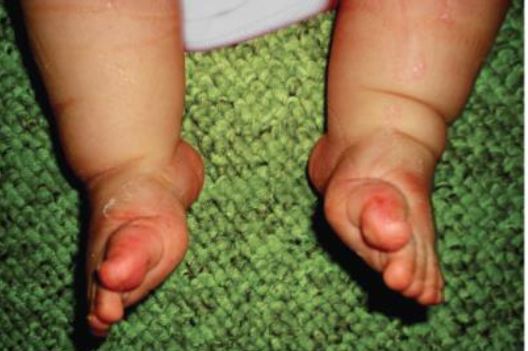
Background: Ponseti method is a well-accepted treatment modality for children with clubfoot deformity. Accelerated frequency of cast changes in Ponseti method may limit the time spent is casts during the corrective phase of treatment without any effect on the final result. We conducted this study to compare the results of accelerated and the conventional Ponseti Method.
Method: A prospective experimental randomized controlled trial was conducted from July 2014 to June 2015. Forty cases with 53 clubfeet were taken up for the study. Half the cases were given biweekly plaster in the accelerated group and the other half weekly casts as per the conventional Ponseti method. All feet were scored using the Pirani method. Successful correction was labeled as Pirani Score <1. Failure was labeled as Pirani Score >1 even after 8 corrective casts. The ‘treatment time in plaster’ refers to the number of days in plaster prior to a tenotomy.
Results: There were no significant difference in the final Pirani score of the two groups. There were no episodes of recurrence at six months. The average duration of treatment in the accelerated group was 15 days whereas in the conventional method was 35 days.
Conclusion: The results of this study support accelerated frequency of cast changes in Ponseti technique. In developing countries where travelling to clinics necessitates time away from home, work, and family, the adoption of ‘accelerated casts’ can reduce the duration of treatment and perhaps help to improve compliance and overall outcomes.
Downloads
References
2. Cooper DM, Dietz FR. Treatment of idiopathic clubfoot: a thirty-year follow-up note. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 1995; 77(10):1477-89.
3. Morcuende JA, Dolan LA, Dietz FR, Ponseti IV. Radical reduction in the rate of extensive orrective surgery for clubfoot using the Ponseti method. Pediatrics 2004;113(2): 376-80.
4. Ponseti IV. Congenital clubfoot: fundamentals of treatment. Oxford, Oxford University Press, 1996.
5. MacNicol M. The management of club foot: issues for debate. J Bone Joint Surg [Br] 2003; 85-B:167-70.
6. Morcuende J, Abbasi D, Dolan L, Ponseti I. Results of an accelerated Ponseti protocol for clubfoot. J Pediatr Orthop 2005;25: 623-6.
7. Harnett P, Freeman R, Harrison WJ, Brown LC, Beckles V. An accelerated Ponseti versus the standard Ponseti method: a prospective randomised controlled trial. J Bone joint Surg [Br] 2011; 93(3): 404-408.
8. Sutcliffe A, Vaea K, Poulivaati J, Evans AM. ‘Fast casts’: Evidence based and clinical considerations for rapid Ponseti method. Foot Ankle Online J 2013;6(9):2
9. Pirani S. Pirani severity scoring. In: Staheli I, ed. Clubfoot: Ponseti management. Third ed. Global-HELP, 2009:27.
10. MacNicol M. The management of club foot: issues for debate. J Bone Joint Surg [Br] 2003;85-B:167-70.
11. Pulak S, Swamy M. Treatment of idiopathic clubfoot by Ponseti technique of manipulation and serial plaster casting and its critical evaluation. Ethiop J Health Sci.2012;22(2):77–84.
12. Janicki JA,Narayan UG,Harvey, et al .Treatment of neuromuscular and syndromic –associated (non-idiopathic ) clubfeet using Ponseti method. J Pediatr Orthop 2009;29(4):393-97.
13. Hegazy M, Results of treatment of idiopathic clubfoot in older infants using Ponseti method:a preliminary report .J Pediatr Orthop B.2009 ;18(2):76-8.
14. Nogueira MP, Ey Battle AM, Alves CG. Is it possible to treat recurrent clubfoot with Ponseti technique after posteromedial release? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009;(467):1298–365.
15. Ullah S, Inam M, Arif M. Club foot management by accelerated Ponseti technique. RMJ. 2014; 39(4): 418-420.
16. Pirani S, Naddumba E, Mathias R, Konde-Lule J, Penny JN, Beyeza T, Mbonye B, Amone J, Franceschi F.Towards Effective Ponseti Clubfoot Care: The Uganda sustainable clubfoot careproject. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2009 ;467(5):1154-1163.
17. Evans AM, Van Thanh D. A review of the Ponseti method and development of an infant clubfoot program in Vietnam. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc 2009; 99: 306–316.
18. Evans AM. Preliminary evaluation of implementing the Ponseti method for correction of clubfoot in Vietnam. J Children's Orthop 2010;4: 553-559.
19. Lourenço AF, Morcuende JA. Correction of neglected idiopathic club foot by the Ponseti method. J Bone Joint Surg [Br] 2007;89: 378-381.
20. Dobbs MB, Gurnett CA. Update on clubfoot: etiology and treatment. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2009 ;467(5): 1146-1153.
21. Ponseti IV, Zhivkov M, Davis N, Sinclair M, Dobbs MB, Morcuende JA. Treatment of the complex idiopathic clubfoot. Clin Orthop Rel Res 2006;451:171-176.
The entire contents of the Orthopaedic Journal of Madhya Pradesh Chapter are protected under Indian and International copyrights. Orthopaedic Journal of Madhya Pradesh Chapter allow authors to retain the copyrights of their papers without restrictions, Authors grant the publisher the right of exclusive publication. The Journal then grants to all users a free, irrevocable, worldwide, perpetual right of access to, and a license to copy, use, distribute, perform and display the work publicly and to make and distribute derivative works in any digital medium for any reasonable non-commercial purpose, subject to proper attribution of authorship. The journal also grants the right to make numbers of printed copies for their personal non-commercial use under Creative Commons Attribution-Non-commercial share alike 4.0 International Public License.

 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative












