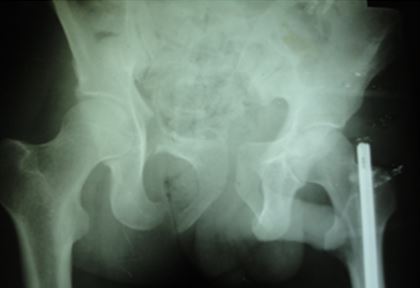
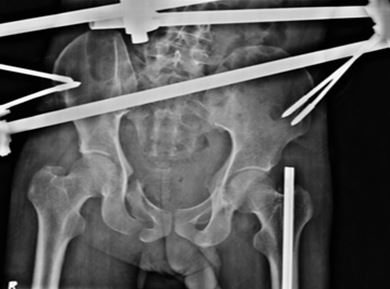
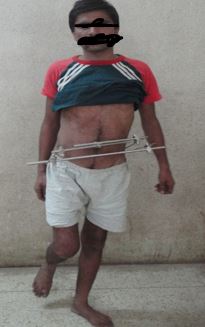
At 6 month follow-up patient can walk, sit and do all his routine work. [ Functional Majeed score 86].
Majeed functional outcome score in surgically treated patient is excellent in 7 patients, good in 4, fair in 2, and poor in 1 patient at 3 month follow-up. Pain is the most common complaint after surgical fixation, it is seen in 4 patients (28.57%) but only 1 patient required change inhis job because of this pain.
Discussion
Historically, pelvic ring injuries, depending on their severity had been treated by a variety of closed methods. Unstable pelvic injuries treated by these conventional measures often result in significant disability, moreover the mortality can reach up to 21.8%.[5,6,7,8] There was a growing body of evidence that the application of an external skeletal frame will reduce venous and bony bleeding and improve tamponade by reducing and maintaining the pelvic volume to the extent that other interventions are rarely required.[4,7,9,10].
Recently, biomechanical studies showed that external frame could not ensure sufficient stability to allow mobilization without the risk of re-displacement of the fragments particularly those with vertical instability. External fixation can be used temporarily in vertically unstable injury as a part of emergency treatment to allow the patient to be placed with trunk in the upright position to improve ventilation [12,13].
External fixation used as definitive fixation in Tile’s type B (partially unstable) pelvic injury. Our results agree with other studies stating that anterior or posterior fixation, or both could restore excellent stability and adequate consolidation of the unstable (Type-C) pelvic injuries with subsequent decrease in morbidity and mortality [6,13,14].
They were mobilized relatively earlier without significant risk of re-displacement of the fragments. Early mobilization minimized the complications associated with prolonged recumbency.
It has been emphasized that surgical treatment should be carried out 5-7 days post trauma when the patient’s general condition allows [13,14] It is the author’s opinion to perform internal fixation for unstable pelvic injuries as soon as the general condition stabilized even up to 6weeks after the injury. The functional results are often affected by the associated skeletal or extra skeletal injuries as well as other variables [5,8,12,13].
Conclusion
Unstable pelvic injury should be treated operatively as soon as general condition of the patient allows. Surgical treatment gives superior results even when performed as late as 6 weeks. External fixation of Tile’s type B unstable fracture allows early mobilization of the patient and avoids early and late complication associated with conservative management.Tile’s type C vertically unstable (>10mm displacement) injury should be treated by internal fixation because an external fixator does not correct the malalignment and is not rigid enough to provide stability in vertical plane.
References
1. Majeed S. A. . ; grading the outcome of pelvic fracture. J. bone and joint. Surg. 71B (2) 304-306, 1989 [Crossref][PubMed][Google Scholar]
2. TornettaP,Dickson K, Matta JM. Outcome of rotationally unstable pelvic ring injuries treated operatively. ClinOrthopRelat Res 1996;329:147-51. . [Crossref][PubMed][Google Scholar]
3. Henderson RC. The long term results of non-operatively treated major pelvic disruption. J Ortho Trauma 1989;3:41-7. . [Crossref][PubMed][Google Scholar]
4. Miranda MA, Rieman BL, Butterfield SL, Burk CJ. Pelvic ring injuries: A long term functional outcome study. ClinOrthopRelat Res 1996;329:152-9. . [Crossref][PubMed][Google Scholar]
5. Goldstein A, Phillips T, Sclafani SJ, Scalea T, Duncan A, Goldstein J et al. Early open reduction and internal fixation of the disrupted pelvic ring. J Trauma 1986; 26: 325-333. . [Crossref][PubMed][Google Scholar]
6. Tile M. Pelvic ring fractures: should they be fixed? J Bone Joint Surg 1988. 70-B: 1-12. . [Crossref][PubMed][Google Scholar]
7. Van den Bosch EW, Van der Kleyn R, Hogervorst M, Van Vugt AB. Functional outcome of internal fixation for pelvic ring fractures. J Trauma 1999; 47: 365-371. . [Crossref][PubMed][Google Scholar]
8. Gruen GS, Leit ME, Gruen RJ, Reitzman AB. The acute management of haemodynamically unstable multiple trauma patients with pelvic ring fractures. J Trauma 1994;36: 706-711. . [Crossref][PubMed][Google Scholar]