Comparative study between dynamic hip screw and trochanteric femoral nail in intertrochanteric femur fracture
Singh V1, Nagle A2*, Patidar A3, Jain A4, Bhinde S5, Agrawal A6, Jain P7
1 V Singh, Department of Orthopaedics, R D Gardi Medical College and CRG Hospital and Associated Charitable Hospital, Ujjain, Madhya Pradesh, India.
2* Ankit Nagle, Resident, Department of Orthopaedics, R D Gardi Medical College and CRG Hospital and Associated Charitable Hospital, Ujjain, Madhya Pradesh, India.
3 A Patidar, Department of Orthopaedics, R D Gardi Medical College and CRG Hospital and Associated Charitable Hospital, Ujjain, Madhya Pradesh, India.
4 A Jain, Department of Orthopaedics, R D Gardi Medical College and CRG Hospital and Associated Charitable Hospital, Ujjain, Madhya Pradesh, India.
5 S Bhinde, Department of Orthopaedics, R D Gardi Medical College and CRG Hospital and Associated Charitable Hospital, Ujjain, Madhya Pradesh, India.
6 A Agrawal, Department of Orthopaedics, R D Gardi Medical College and CRG Hospital and Associated Charitable Hospital, Ujjain, Madhya Pradesh, India.
7 P Jain, Department of Orthopaedics, R D Gardi Medical College and CRG Hospital and Associated Charitable Hospital, Ujjain, Madhya Pradesh, India.
Introduction: The incidence of intertrochanteric fracture has been rising with an aging population in many parts of the world and the number of hip fractures is expected to increase year after year. Reduction of fracture is the goal of treatment so that near anatomic alignment and normal femoral anteversion are obtained. Surgical treatment with stable reduction and fixation allows early mobilization and reduces complications. There are two main types of fixations for intertrochanteric fractures- the extramedullary plate fixation and intramedullary nail.
Aims and Objective: The main objective of this study was to compare outcome of Dynamic Hip Screw and Trochanchanteric Femoral Nail in patients of intertrochantric femur fracture.
Material and Methods: In this study, 50 patients of intertrochanteric fracture were admitted and randomly divided into two groups. 25 patients operated with Dynamic Hip Screw and other 25 were undergone Trochanteric Femoral Nail fixation. Outcome after the surgery such as average duration of surgery, blood loss, hospital stay and functional outcome were assessed using Harris Hip Score.
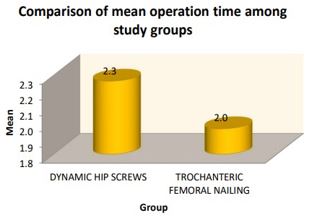
Results: The study findings reveal that there was a significant difference in mean operative time between both study groups with p<0.05. Hence in dynamic group mean operative time was 2.26±0.44 hours and in trochanteric femoral nailing mean operative time was 1.96±0.2 hours. Blood loss was more significant in patients with DHS as compared with TFN p<0.05. In dynamic group mean Harris score was 81.76±9.49 and in trochanteric femoral nailing mean Harris score was 87.12±7.74.
Conclusion: Surgical management of intertrochanteric fractures is the preferred treatment to avoid complications of prolonged immobilization. Dynamic Hip Screw (DHS) has been the gold standard. Our study indicates that TFN may be better choice when compared to DHS in unstable intertrochanteric fractures.
Keywords: Dynamic Hip Screw, Trochanteric Femoral Nail fixation, Intertrochanteric fracture
| Corresponding Author | How to Cite this Article | To Browse |
|---|---|---|
| , Resident, Department of Orthopaedics, R D Gardi Medical College and CRG Hospital and Associated Charitable Hospital, Ujjain, Madhya Pradesh, India. Email: |
Singh V, Nagle A, Patidar A, Jain A, Bhinde S, Agrawal A, Jain P, Comparative study between dynamic hip screw and trochanteric femoral nail in intertrochanteric femur fracture. ojmpc. 2023;29(2):54-59. Available From https://ojmpc.com/index.php/ojmpc/article/view/179 |